|
Large Language Models (LLMs) can play a significant role in Threat Intelligence, which involves the collection, evaluation, and analysis of information about potential security threats. Here are several ways LLMs contribute to this field:
Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: LLMs can process vast amounts of data from various sources, including social media, dark web forums, and news articles. They are adept at recognizing patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential threats. Threat Intelligence Reports: They can assist in generating comprehensive threat intelligence reports. By analyzing data, they can help in summarizing trends potential threats, and recommend strategies to mitigate these risks. Natural Language Understanding: LLMs' ability to understand and interpret human language makes them valuable in analyzing texts for potentially malicious content. This includes understanding the context of discussions on online platforms that might be related to cybersecurity threats. Automated Alerts and Notifications: They can be programmed to automatically alert analysts about potential threats detected through their analysis, speeding up the response time. Enhancing Human Analysts' Work: By handling routine data analysis tasks, LLMs free up human analysts to focus on more complex aspects of threat intelligence that require human intuition and experience. Phishing Detection: LLMs can assist in identifying phishing attempts in emails and messages by analyzing the text for common phishing indicators. Trend Analysis and Predictive Insights: They can help in identifying emerging trends in cybersecurity threats, allowing organizations to prepare or respond proactively. Customized Threat Intelligence: LLMs can be tailored to the specific needs of an organization, focusing on particular types of threats or industry-specific risks. Training and Simulation: They can be used to create realistic cybersecurity training scenarios and simulations, helping security professionals to improve their skills. Integration with Other Technologies: LLMs can be integrated with other AI and machine learning tools, enhancing overall threat intelligence systems. However, it's important to note that while LLMs are powerful tools, they should be used as part of a broader strategy that includes human expertise and other technological solutions. Their effectiveness is also dependent on the quality of the data they are trained on and their ability to adapt to evolving threats.
0 Comments
 MongoDB recently experienced a significant data breach that has raised concerns in the cybersecurity community. Timeline and Discovery The breach was detected on the evening of December 13, 2023. MongoDB noticed suspicious activity on its corporate systems, which led to an immediate investigation. Nature of the Breach The attackers gained unauthorized access to MongoDB's corporate systems. This led to the exposure of customer account metadata and contact information. Importantly, there is currently no evidence to suggest that data stored in MongoDB Atlas, the company's cloud database service, was affected. Response and Communication MongoDB's Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Lena Smart, sent an email to MongoDB customers, detailing the breach and urging caution against potential social engineering and phishing attacks. MongoDB has activated its incident response process and is conducting a thorough investigation of the breach. They have also notified relevant authorities. Precautionary Measures
Additional Issues Following the breach, MongoDB reported a spike in login attempts, which caused issues for customers trying to access MongoDB Atlas and the Support Portal. However, the company clarified that this was not related to the security incident. Ongoing Investigation MongoDB is still investigating the incident and is expected to provide further updates as they continue to uncover more details. Implications This breach is significant given MongoDB's role as a leading database management company. The exposure of customer account metadata and contact information is a serious concern, as it could potentially be misused. The breach serves as a stark reminder of the constant threats faced by digital companies and underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has alleged that SolarWinds concealed cybersecurity defense issues before a December 2020 attack linked to APT29, the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) hacking division. Hackers found a way to insert malware into a version of the company's Orion IT monitoring application, allowing Russian operatives to gain a foothold in high-value targets. They used the access to deploy additional malware to compromise internal and cloud-based systems and steal sensitive information over several months. The SEC claims that its CISO Timothy G. Brown was aware of the cyber security risks and poor practices, but SolarWinds failed to notify its investors. Instead, the company reportedly disclosed only broad and theoretical risks to its investors. SEC says a Solar Winds Internal Document that the engineering teams could no longer keep up with a long list of new security issues they had to address.SolarWinds has denied the SEC's charges and says it deliberately chose to speak candidly and frequently about security by sharing what it learned to help others become more secure. This lawsuit marks the first time the SEC has held a CISO personally accountable for cybersecurity failures. The charges will reignite concerns among CISOs about the liabilities associated with the role. Source CISO/Security Leaders Dilemma - The general viewpoint is the CISO is responsible for all the security issues. Still, in practice, CISOs often need more power and authority to get things issues fixed. In most organizations, the CISO will report to the CLO, CTO, or CRO, which is counterproductive. The CISO should report directly to the CEO and the board of directors' cybersecurity committee to be effective. It's well-known in the industry that the CISO does not get the same Compensation indemnity as the other benefits that the other leaders, like the CEO or CPO, get. The reality is that without any significant incidents, business leaders often see information security as a cost center. In most cases, the CISO and the Security Leadership team are aware of significant security gaps. The critical issue is that the business leadership does not prioritize the security issues as it's not revenue-generating efforts. Vulnerability Management, Bug Bounty, Appsec, Pentest, Red team, and CSIRT Teams detect many security gaps quickly. Still, they often hear that the sheer volume of security issues being identified is much higher than the capacity of Engineering teams to resolve them. Often, project managers deprioritize the security issues over the new features. To Solve this, Leaders should implement a couple of following things:
Okta Support System was compromised, allowing unauthorized access to the sensitive HTTP Archive (HAR) files uploaded by the Customers. HAR Files contain sensitive data like Session Token, which the Okta Support team uses for impersonation. The Threat Actor used HAR Files to gain access to the system. In March 2022, Okta disclosed an internal system breach from the hacking group LAPSUS$. In a recent attack, the Okta team has not yet revealed the name of the threat actor, but they believe this is an adversary they have seen before. Timeline
Attacker Techniques - Kill Chain
Supply Chain Breaches
Recommendations
Questions for CISO's & Security LEaders?
The sheer volume of data generated is staggering in the modern digital landscape. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, it becomes crucial for organizations to store, analyze, and derive insights from this data to bolster security. Enter the concept of the Security Data Lake. What is a Security Data Lake?A Security Data Lake is a centralized repository that allows organizations to store structured and unstructured data at any scale. Unlike traditional databases, which are designed to store structured data, a data lake can store vast amounts of raw data in its native format until needed. When we apply this concept specifically to cybersecurity, the data lake is optimized to collect, store, and analyze massive volumes of security event data, logs, threat intelligence feeds, and more. This setup enables advanced analytics, correlation, and threat detection. Key Features:
When we think of threats to our businesses, the image that might come to mind is a masked hacker typing away in a dimly lit room, infiltrating our systems remotely. Yet, a less conspicuous but equally dangerous adversary exists, the insider threat.
What is an Insider Threat?An insider threat arises when someone within the organization who has inside information concerning its security practices, data, and computer systems misuses, which somehow leads to harm to the organization. This can encompass employees, former employees, contractors, or business partners. Why is it Significant?Unlike external threats, insiders have access to critical systems and data. They understand the internal processes, know the weak spots, and can exploit them effectively. Insiders may inadvertently leak sensitive information, while others might have malicious intentions driven by personal vendettas, financial gain, or espionage. Types of Insider Threats:
By staying informed, leveraging technology, fostering open communication, and building solid relationships with employees, businesses can prevent insider threats and create an atmosphere of trust and collaboration. In the digital age, where data is a prized asset and threats lurk around every corner, disregarding insider threats is not an option. It's crucial to acknowledge, understand, and actively work against these risks to safeguard the future of any organization. Data Exfiltration and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is one of key topic of our discussion today. One of the ways to detect APT Groups and advanced ransomwares at early stage is by analyzing the outbound traffics. Most of the advanced treats will try to establish a C2 connection.
Profile 'outbound' traffic data:
Some outliers can be:
Dashboards are the good starting point.With the flow data you can develop a 'Top Level Domain(TLD) Dashboard' and look for following traffic patterns:
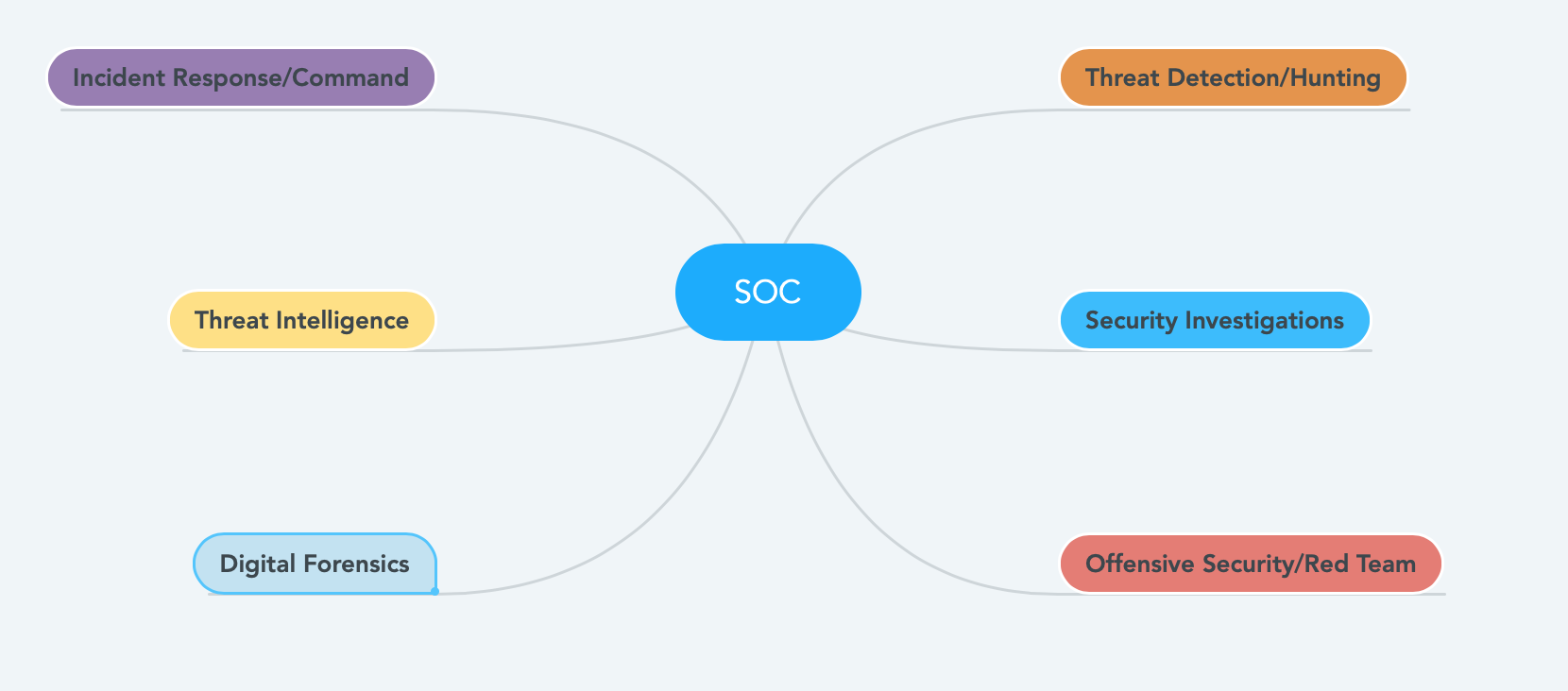
#Comment if you have additional tips. I have to build many SOC teams in my professional career. In this post, I’d like to declutter some of the myths about SOC. Let’s start with the basics. One of the most important questions is why your organization needs a SOC? Enterprise often collects a large amount of data in the form of logs. Simply storing the data is not valuable. The humongous amount of information needs to be searched for malicious activities. If there is malicious activity, you need a human to respond to it intelligently. SOC team members will do the Detection, Investigation, and Response to the incident. Another critical aspect of the SOC team (often overlooked) is the post-incident reviews. What are the sub-team/sub-group in a SOC? Key Roles in a SOC Team?
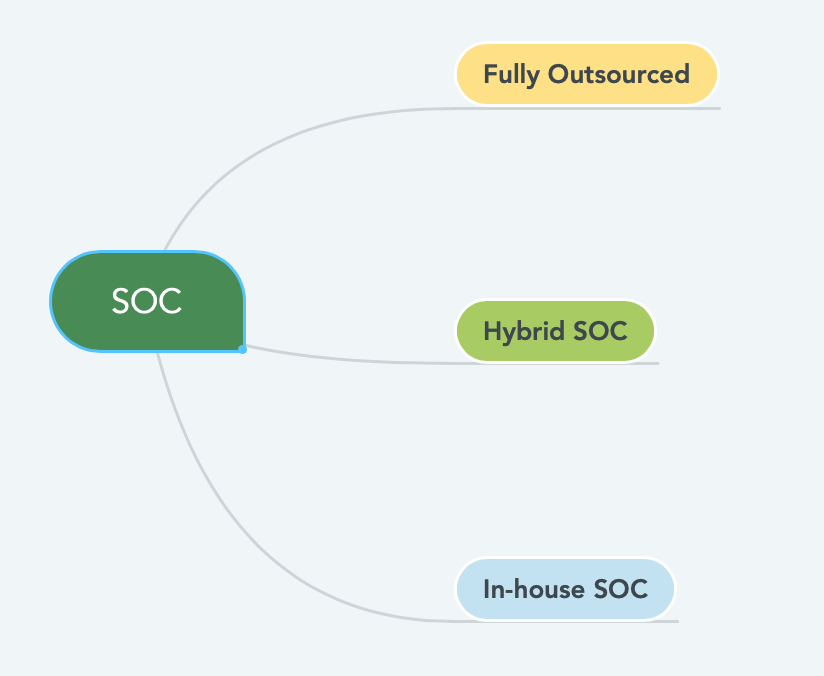
Types of Security Operation Center (SOC) Fully Outsourced SOC: Hiring, Building, and retaining SOC Teams are challenging and expensive. There are not a lot of experienced Cyber Security Analyst and Engineers out there in the market. It’s honestly a new career option. To avoid the hassle, the organization often decide to outsource the security operation fully to Managed Security Service Providers (MSSP).
There are a few advantages and disadvantages of having a fully outsourced SOC. The most significant benefit is the speed; you can have someone start looking at your data/alerts as soon as you sign the contract.In there is any anamoly, MSSP will do the hunt, investigation and escalated it to you pretty quickly. The biggest downside is the knowledge gap. All the knowledge/intelligence about your network/endpoint stays with the MSSP. As soon as you cancel the contract, it’s gone. Another significant disadvantage is the MSSP is expensive. You have to pay a lot of money out of your budget for the SOC. In some cases, the quality of the investigation can be poor too. Even after outsourcing your SOC, mitigating a malicious and compliance stays with the organization only. Usually, companies in the early stage will go for this model. MSSP will care more about the SLA’s rather that the quality of the investigation. If you are adopting this model, please ensure to discuss all the norms upfront, including the resume/profiles fo the Analysts. Hybrid SOC: It’s a combination of the MSSP + In-house SOC team. Usually, the Detection, response, and forensics team will be in-house, and the Tier-1 & 2 Analyst will outsource. The majority of the pros and cons of MSSP mentioned above applies here as well. The benefit is you keep your institutional knowledge. If your want to run your SOC 24/7 and your security team is only in one country this model will be helpful in terms of coverage and control. In-house SOC: Fully In-house SOC Teams are high, usually big size organizations with big budgets will go for this model. I’d say having a functional in-house SOC is a sign of maturity of an overall cybersecurity program. If your company is global, you may want to have your SOC team in mutiple time zones. Key Responsibilities of SOC
In this blogpost, we will discuss about the high quality Open source NSM Tools. Security Onion is one of the most common and popular NSM distribution.
Security Onion has Ubuntu based Linux distribution. It comes with a bunch of softwares:
Web Sessions are usually managed by a "Session Token". Session hijacking is a way of exploiting the web session control mechanism.It's a way to get an unauthorized access to the web-server by stealing a valid token.
Session Hijacking is a type of attack and it can use accomplished by using various techniques like Session Sniffing, Clint Side Attacks like XSS, Man in the middle/browser type of attacks. |


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed