|
MacOs Key Chain Analysis
Location: ~Library/Keychains File of interest: keychain-2.db Data in Login & System Keychain can be very useful in an investigation. Once you copy the keychain-db file - you can use keychain native app to view the content. $ cd /Users/<Username>/Library/Preferences
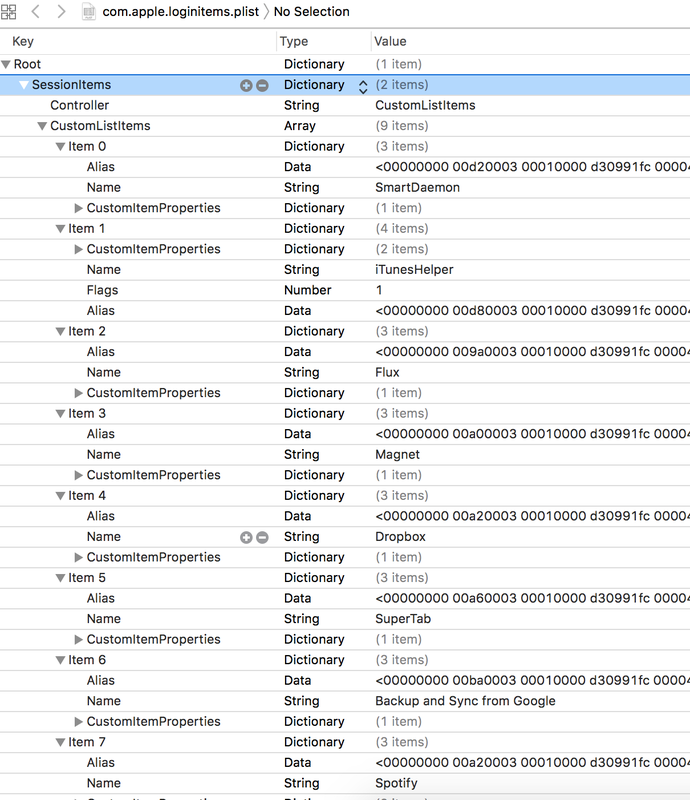
$ open -a xcode com.apple.loginitems.plist You can use any hex editor to read the hex data. Hex will give you the location of the file path of the login item. https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1t6swpG1kN_8ZP6BX3CkEeOyUmsAv86pqU5yEvwIdAP0/edit?usp=sharing
Location: /Users/<username>/Library/KeyboardServices/TextReplacements.db
The data from this DB can be very handy in investigation ot get access to the suspects' machine. Following plist hold the information of the application that get start at the system boot:
open -a xcode ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginitems.plist Launch Agents (User Level) - Background User Process
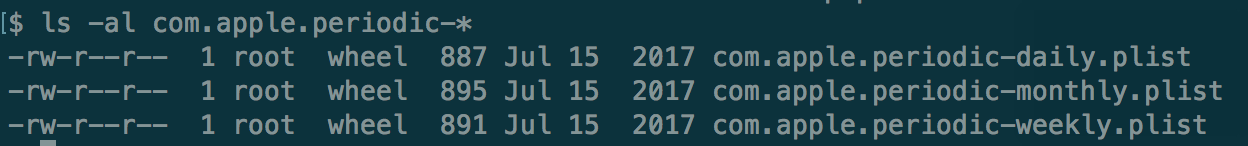
$ cd /System/Library/LaunchAgents/ $ cd /Library/LaunchAgents/ Launch Deamons (System Level) - Background System Process cd /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ $ cd /Library/LaunchDaemons/ This is basically like a cron jobs.Best examples of Launch Daemons are following plist files: Bash History file is very useful for investigation purposes.
Location: /Users/<username>/.bash_history - Usually it stores upto last 500 Bash Command but sometimes in live response/collection - you may get little more.
Antedating: Creating a document with incorrect time stamps.
Investigation:
How to antedate a document?
Readings: http://www.cse.scu.edu/~tschwarz/COEN252_13/Papers/antedating.pdf |
ArchivesCategories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed