|
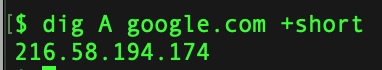
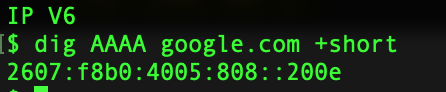
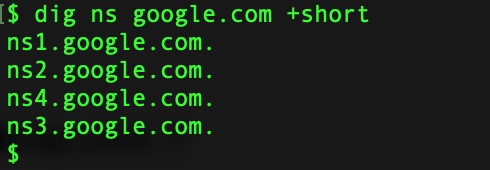
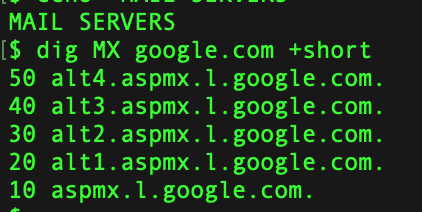
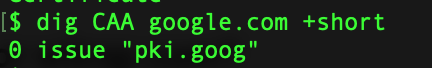
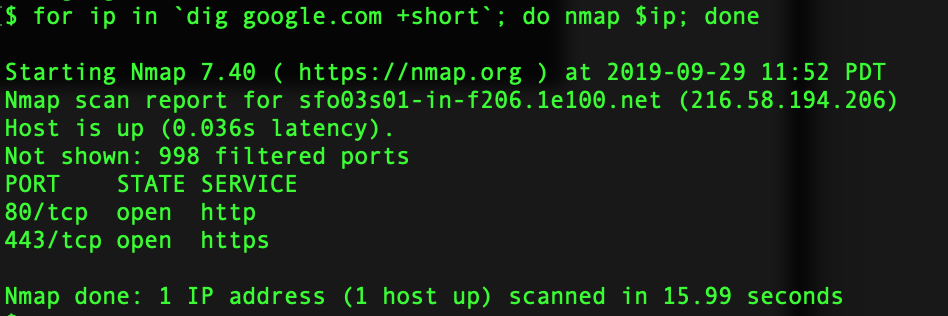
Dig is one of the more popular command to enumerate the information about a DNS Record.Lets see it in action. Get IPv4 Infomation about the domain Get IP v6 Information Get Information about Name Servers Mail Server Information Certification Info Running Dig with Nmap Couple of GUI based tools you can use for this purpose are as follows:
In this post, we are going to discuss about how linux handles hardware and interact with them via command-line. udev service, is responsible for managing linux devices.
All information related to the hardware is in the /dev pseudo file system. We will run the following commands to understand it in detail. lspci - Displays Information of PCI Devices Attached lsusb - Displays Information on USB Devices Attached lscpu - Displays Information on Processes on a System lsblk - Displays information on all block devices on the system Linux kernel is the core framework of the operating system with any Linux operating system typically known as the GNU/Linux operating system.
The Linux kernel provides a way for the rest of the system to operate with its hardware that's connected to it. All the memories, such as the hard disk and the ram, has plugged into the system. The networking capabilities of the computer and, of course, itself. And what we mean by itself is the kernel's ability to communicate with this various subsystems. The Linux kernel is known as a monolithic kernel, and what that means is that the kernel handles all memory management and hardware device interactions by itself. Also, extra functionality can be loaded and unloaded dynamically through kernel modules. A monolithic kernel ensures that the system will not need to be rebooted into a different kernel image for added functionality. Command for Linux Kernel Module
In this post, we're going to take a look at pseudo file systems.
What is a pseudo file system? File system is a method of laying off files and folders on a physical hard disk. Within Linux, every file and folder is actually nothing more than just a file itself. The hard drive, network information, keyboard, display monitor. Everything is seen as a file within Linux. A pseudo file system, on the other hand, does not exist on a physical hard disk. It actually is created by the Linux Kernel after the computer boots up, and it only exists and RAM while the system is up and running. Once you shut your computer off, that file system no longer exist as it gets wiped out when the RAM is cleaned. When your system boots up, the kernel would create another pseudo file system, using the same directories that will hold all of the information that the kernel in a system uses. There are multiple pseudo files systems that are used within Linux, but the two main ones are
List all the AWS S3 Buckets
aws s3api list-buckets --query "Buckets[].Name" See if you can get a response from an AWS endpoint curl <ip:port> -s | xmllint --format - Access Public S3 Bucket: aws --endpoint <url:port> --no-sign-request s3 ls s3://public you can use 'cp' command to copy the data to your local machine. |
Archives
April 2020
Categories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed