|
Timestamp is extremely important in forensic investigation - Created (Birthdate): File volume creation date/time - Accessed: Last time File Data was Opened - Modified: Last Time file Data was Changed - Changed (Change in Metadata): Master file table entry was changed or changes in file attribute. You can remember it as B-MAC NTFS stores Time in UTC while FAT store time in Local Time. Windows Timestamp file is located in $MFT (located in Root of NTFS) $MFT Keep Tracks of all files along with Metadata. $Standard_Information($SI) $FILE_NAME($FI) Things to do when you suspect if the file timestamp is modified:
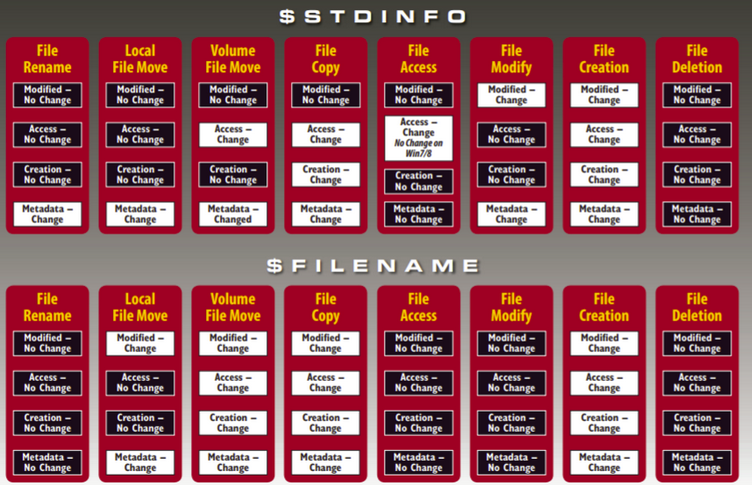
The above image is taken from Cyber Forensicator website. Please click on image to read the whole article.
Resources: https://www.defcon.org/images/defcon-19/dc-19-presentations/Lenik/DEFCON-19-Lenik-MAC(b)Daddy.pdf https://digital-forensics.sans.org/blog/2010/11/02/digital-forensics-time-stamp-manipulation http://cyberforensicator.com/2018/03/25/windows-10-time-rules/ Windows Forensics:
Cache Memory and History Analysis: IE:
Firefox: Md5 Hash
Pfirewall.log Windows Password: Active Directory - NTDS.DID – For a System is SAM (System Account Manager) File – System32 Config, Additional Copy in repair folder.
NTLM V2 is the latest version used by windows: Sigverif: Shows unsigned drivers
|
Archives
September 2019
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed