|
Shimcache/Amcache is also know is AppCompatCache. There are certain application which are build to work on the historical version of the OS. Usually if an application needs 'shimming' - windows looks at AppCompatKey registry key to figure out if an application needs shimming or not. When a program is shimmed, a registry key is updated to notify the system. Use tools like RegRipper to parse it.
Forensics Value: If you are dealing with an Anti-forensics kind of situation. The adversary might have deleted the logs from prefetch and the file itself. The amcache entries will show if the app existed on the system. Key things to remember:
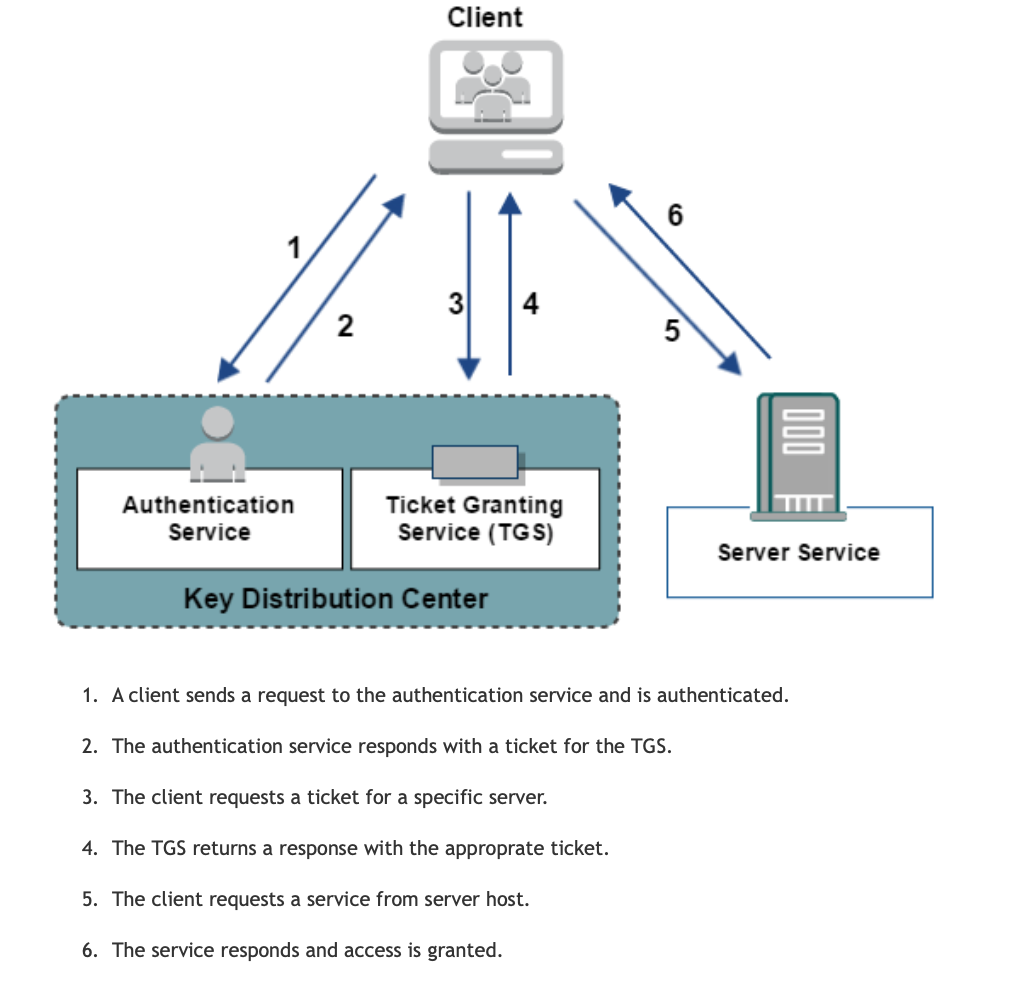
Shimcache/Amcache and Prefetch is a very powerful combination for identification of the execution. Things to keep in mind during shimcache analysis: 1) Each time an exe is modified or renamed - it'll create a new shimcache entry 2) Cannot determine the last time of execution via Shimcache.  Kerberos is a network authentication protocol inspired by the greek work for a a three heaed dog Cerberus. Couple of key points to remember about the protocol
Source: https://docops.ca.com/ca-single-sign-on/12-8/en/configuring/policy-server-configuration/authentication-schemes/configure-kerberos-authentication Kerberos Attacks#Pass the ticket:
Ways to investigate Pass the ticket Attack
Countermeasures:
In overpass-the-hash, the attacker will try to capture NTLM hash for the account it wishes to compromise using tools like Mimikatz etc. Using this command in mimikatz: Sekurlsa::pth /user:[USER] /domain:[DOMAIN] /ntlm:[NTLM HASH] The NTML hash was passed into Kerberos authentication provider using RC4 Encryption #Kerberoasting: The focus of this attack is to compromise a service account. It request a ticket for a highly privileged service account. Capture the hash for it and crack it offline. #Golden Ticket: This is generated with a Ticket Granting Ticket for any account with my expiration is generated. Majority of the Active Directory based attacks can be detected by implementing Microsoft Advanced Threat Analytics. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/advanced-threat-analytics/what-is-ata Windows Forensics:
Cache Memory and History Analysis: IE:
Firefox: Md5 Hash
Pfirewall.log Windows Password: Active Directory - NTDS.DID – For a System is SAM (System Account Manager) File – System32 Config, Additional Copy in repair folder.
NTLM V2 is the latest version used by windows: Sigverif: Shows unsigned drivers
|
Archives
September 2019
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed