|
I want to share my recent preparation and GCFA exam experience. I took the SANS FOR-508 Course a while ago. I have following tips for you if you are planning to prepare for GCFA Exam.
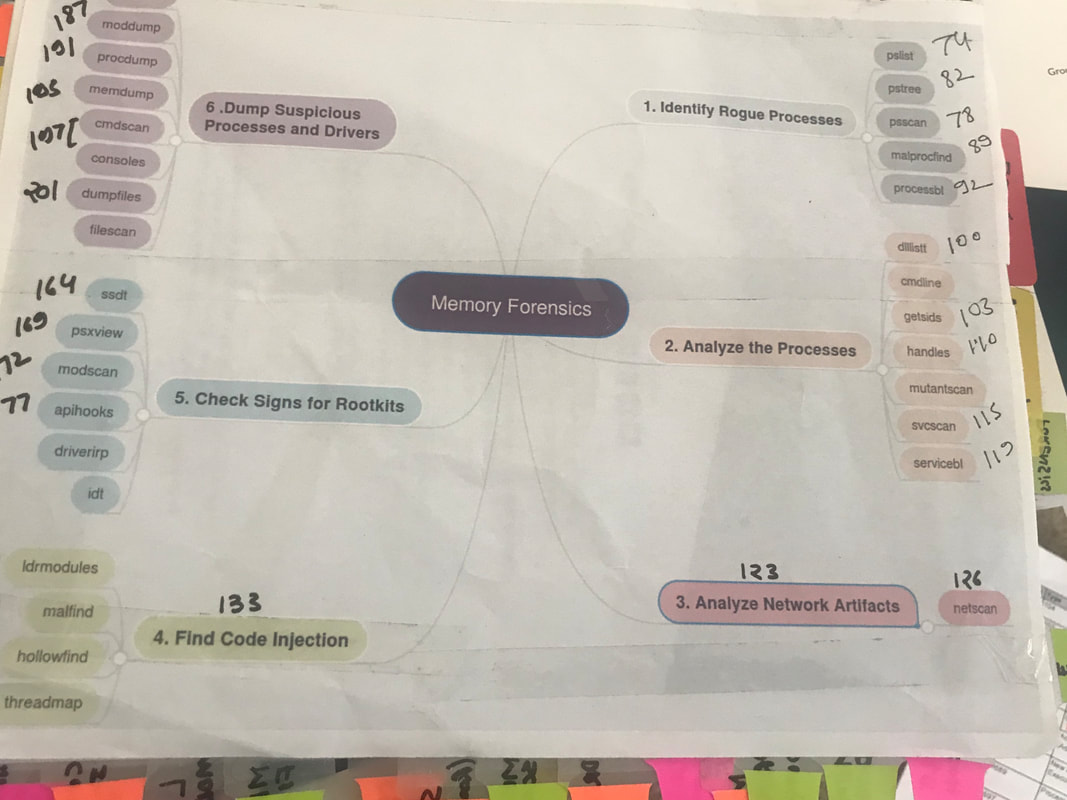
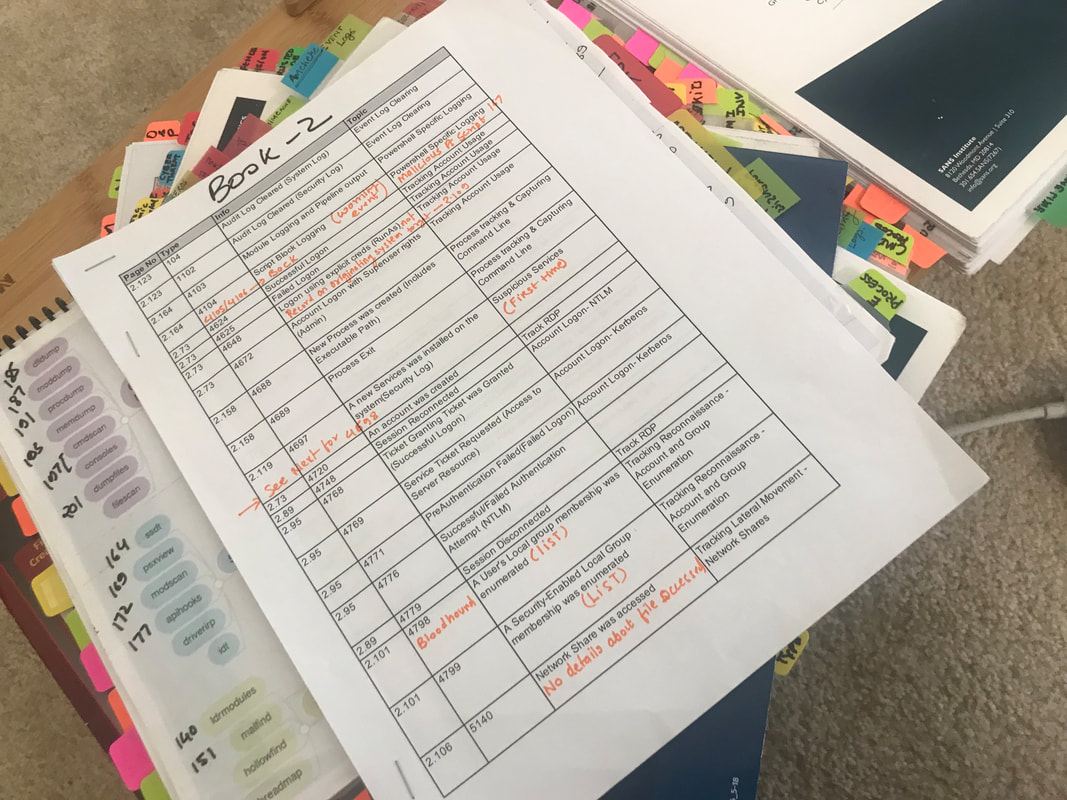
Learn about the pattern of the exam from this link: https://www.giac.org/certification/certified-forensic-analyst-gcfa • 115 questions in 3 hours are challenging ~ 1 minute and 30 seconds for each question. • Passing percentage is 71%; therefore, you need to get ~82 questions right • GCFA will test your detailed understanding of the material like Key Concepts, Facts, Tools, and other granular details mentioned in the SANS FOR 508 Books. • It's challenging to find and answer a question in 1 minute 30 seconds. You'll need a way to search the content quickly. • Read all the books 2-3 time, highlight the essential things, and add the keywords/definition to your index. • Make a useful index - there are two methods. 1) https://tisiphone.net/2015/08/18/giac-testing/ 2) Make an index with keyword, definition, page-number, book number, and sort it alphabetically. • Make Mind-Maps and glue it on the back of each book (example below) • SANS Posters works as a quick reference guide. Carry all FOR 508 related posters • Take the Practice Test as you are taking an actual exam. It's just like an exam simulation, and the level of the practice test is similar to the real exam. • I'd also recommend you to practice SANS FOR-508 Workbook to understand all the concepts in a better way. The exam is designed to test your expertise and comprehension of the material. Feel free to reach out to me if you have any additional questions. NTFS was designed to overcome the shortcomings of FAT Filesystem. Some common features are:
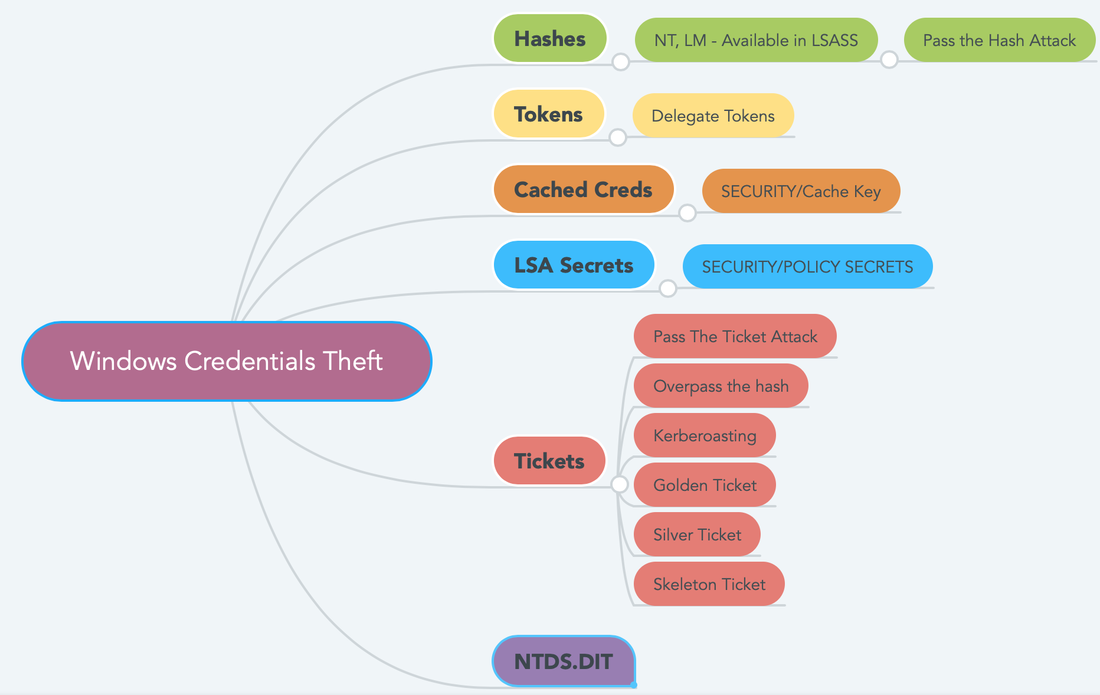
NTFS Transaction Logging / Journling: - NTFS uses a LOG FILE to record changes in the metadata to keep track of state and integrity. This allows to them to understand the system crashes in better way. USN (Update Sequence Number)/Change Journal: - NTFS keep track of all the files that have changed on the system by USN (Update Sequence Number) Journal or Change Journal. This is a great feature for the tools like antivirus scanners or backup tools. They only have to scan/review the changes/updates items and can perform incremental pass over the drive. POSIX:- NTFS Supports hard and soft links. Hard link is a single file respond to multiple name.In soft links the another copy gets created but doesn't have data in it just like an alias. Object ID:- NTFS uses Object ID to track certain files. You can move the files freely, rename it. etc. The distrubuted link tracking system will update all the links to the file and you'll never lose it. File Level Encryption:- It implements file level encryption. Because of this feature you are not able to easily read the files of other uses. Volume Shadow Copy:- NTFS keeps a backup of your files via the Volume Shadow Copy Feature. Alternate Data Stream:- Files in windows can have additional content. For example: Files downloaded from internet can be tagged and windows can give you warning before executing it. We will discuss about Windows Credentials Theft in the blog post. This is the first thing any attacker will do after exploiting to your network. The aim of the attacker will be to gather the credentials for privilege escalation and lateral movement. Companies do not pay much attention to the account and password management and adversaries do take advantage of it. See the mind-map below to understand the top categories.
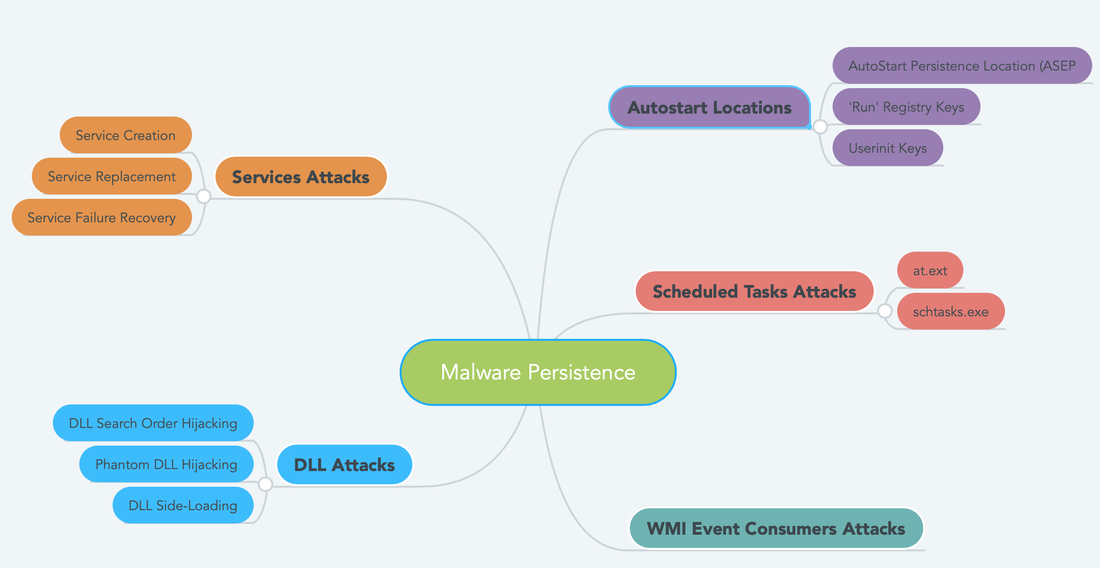
Windows Services Attacks:
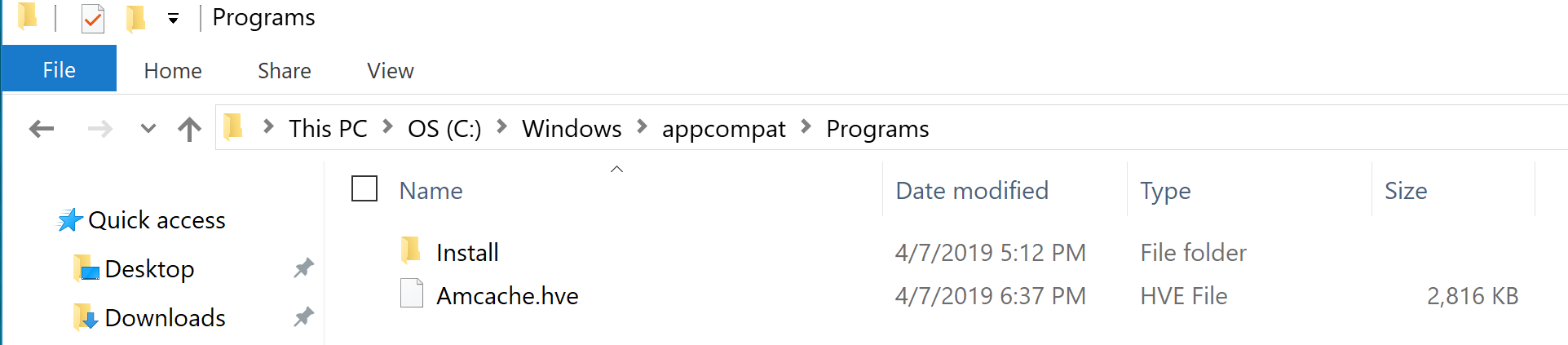
Service Creation: Malware authors utilized windows services to maintain the persistence in the machine. There are some services that can be started at the boot by configuring the start type value by manually or by some event. Windows has tons of services, malware author utilized the concept of "Hide in Plain Sight". Once the attacker has admin rights he/she can easily create a new service or modify an existing one. Service Replacement: Malware author will find an unused service and replace it with a malicious executable and set it to autostart. Service Recovery Mode: Load a malicious services and an existing service crashes Shimcache/Amcache is also know is AppCompatCache. There are certain application which are build to work on the historical version of the OS. Usually if an application needs 'shimming' - windows looks at AppCompatKey registry key to figure out if an application needs shimming or not. When a program is shimmed, a registry key is updated to notify the system. Use tools like RegRipper to parse it.
Forensics Value: If you are dealing with an Anti-forensics kind of situation. The adversary might have deleted the logs from prefetch and the file itself. The amcache entries will show if the app existed on the system. Key things to remember:
Shimcache/Amcache and Prefetch is a very powerful combination for identification of the execution. Things to keep in mind during shimcache analysis: 1) Each time an exe is modified or renamed - it'll create a new shimcache entry 2) Cannot determine the last time of execution via Shimcache. Antedating: Creating a document with incorrect time stamps.
Investigation:
How to antedate a document?
Readings: http://www.cse.scu.edu/~tschwarz/COEN252_13/Papers/antedating.pdf Prefetch Basics: Windows Prefetch stores application specific data in order to help it to start quicker. Each time you turn on your computer, Windows keeps track of the way your computer starts and which programs you commonly open. Windows saves this information as a number of small files in the prefetch folder. The next time you turn on your computer, Windows refers to these files to help speed the start process.
The os loads key pieces of data and code from disk into memory before it's actually needed. Location: c:\Windows\Prefetch Prefetch Investigation FAQ: When you should grab prefetch file? You can grab is before performing Incident Response as the prefetch directory is populated after the application is executed. The content of the file is pretty volatile. How you can use it in an Investigation? Analysis of prefetch file is common in investigation, it has wealth of information stored in it. * It contains:
Here is what information we can glean from the prefetch:
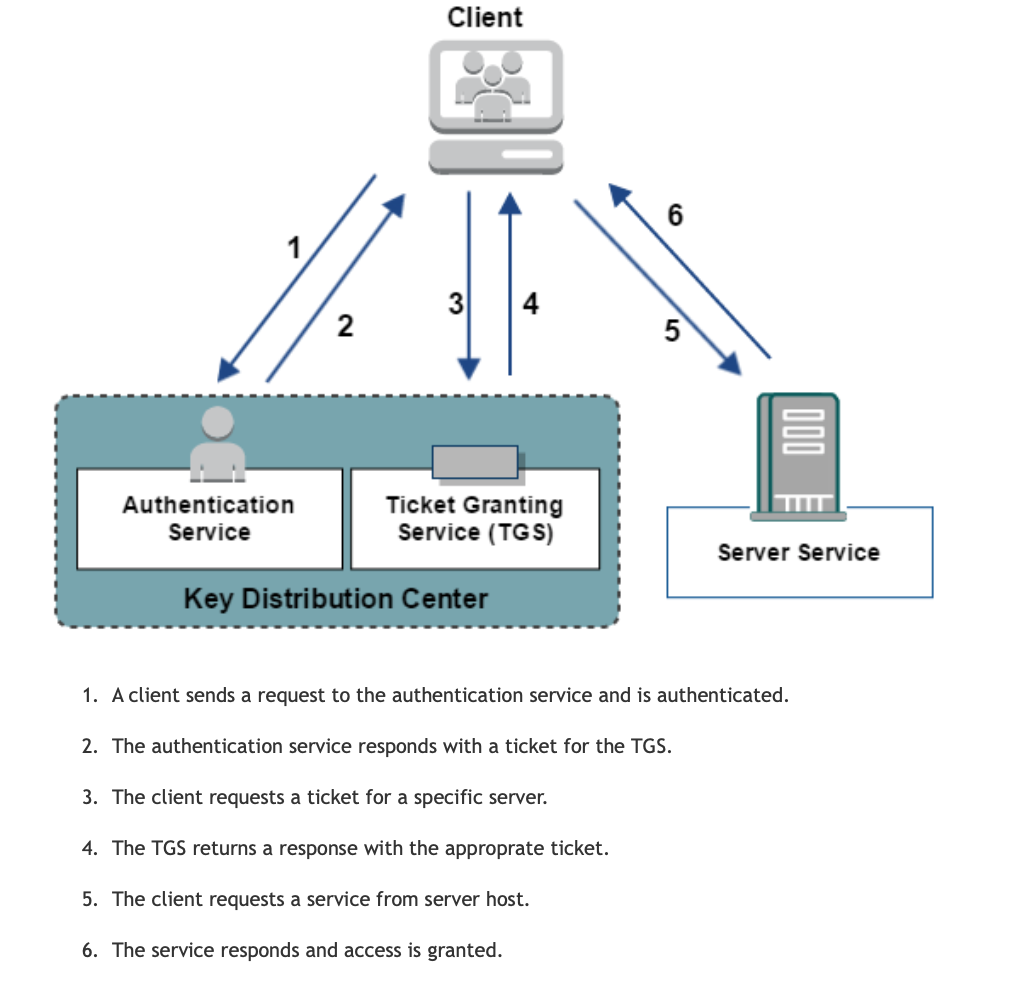
 Kerberos is a network authentication protocol inspired by the greek work for a a three heaed dog Cerberus. Couple of key points to remember about the protocol
Source: https://docops.ca.com/ca-single-sign-on/12-8/en/configuring/policy-server-configuration/authentication-schemes/configure-kerberos-authentication Kerberos Attacks#Pass the ticket:
Ways to investigate Pass the ticket Attack
Countermeasures:
In overpass-the-hash, the attacker will try to capture NTLM hash for the account it wishes to compromise using tools like Mimikatz etc. Using this command in mimikatz: Sekurlsa::pth /user:[USER] /domain:[DOMAIN] /ntlm:[NTLM HASH] The NTML hash was passed into Kerberos authentication provider using RC4 Encryption #Kerberoasting: The focus of this attack is to compromise a service account. It request a ticket for a highly privileged service account. Capture the hash for it and crack it offline. #Golden Ticket: This is generated with a Ticket Granting Ticket for any account with my expiration is generated. Majority of the Active Directory based attacks can be detected by implementing Microsoft Advanced Threat Analytics. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/advanced-threat-analytics/what-is-ata Overview:
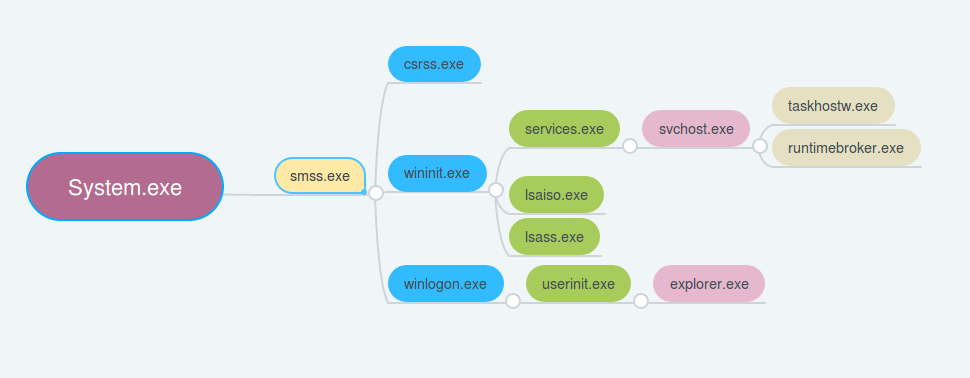
An application consists of one or more processes. A process, in the simplest terms, is an executing program. One or more threads run in the context of the process. A thread is the basic unit to which the operating system allocates processor time. A thread can execute any part of the process code, including parts currently being executed by another thread. Each process provides the resources needed to execute a program. A process has a virtual address space, executable code, open handles to system objects, a security context, a unique process identifier, environment variables, a priority class, minimum and maximum working set sizes, and at least one thread of execution. Each process is started with a single thread, often called the primary thread, but can create additional threads from any of its threads. System
smss.exe
csrss.exe
isaiso.exe
explorer.exe
wininit.exe
lsass.exe
taskhostw.exe
|
Archives
September 2019
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed